Starch-Based Polymer Materials as Advanced Adsorbents for Sustainable Water Treatment: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 37514503
- PMCID: PMC10385024
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15143114
Starch-Based Polymer Materials as Advanced Adsorbents for Sustainable Water Treatment: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
Over the past three decades, chemical and biological water contamination has become a major concern, particularly in the industrialized world. Heavy metals, aromatic compounds, and dyes are among the harmful substances that contribute to water pollution, which jeopardies the human health. For this reason, it is of the utmost importance to locate methods for the cleanup of wastewater that are not genuinely effective. Owing to its non-toxicity, biodegradability, and biocompatibility, starch is a naturally occurring polysaccharide that scientists are looking into as a possible environmentally friendly material for sustainable water remediation. Starch could exhibit significant adsorption capabilities towards pollutants with the substitution of amide, amino, carboxyl, and other functional groups for hydroxyl groups. Starch derivatives may effectively remove contaminants such as oil, organic solvents, pesticides, heavy metals, dyes, and pharmaceutical pollutants by employing adsorption techniques at a rate greater than 90%. The maximal adsorption capacities of starch-based adsorbents for oil and organic solvents, pesticides, heavy metal ions, dyes, and pharmaceuticals are 13,000, 66, 2000, 25,000, and 782 mg/g, respectively. Although starch-based adsorbents have demonstrated a promising future for environmental wastewater treatment, additional research is required to optimize the technique before the starch-based adsorbent can be used in large-scale in situ wastewater treatment.
Keywords: adsorbent; dye; heavy metals; micropollutants; oil; organic solvents; pesticides; pharmaceutical pollutants; starch; wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
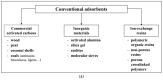

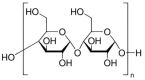
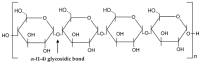
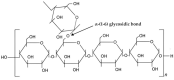


Similar articles
-
Polysaccharide nanocomposites in wastewater treatment: A review.Chemosphere. 2024 Jan;347:140578. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.140578. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Chemosphere. 2024. PMID: 37939921 Review.
-
Starch-based hydrogels for environmental applications: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jun;269(Pt 2):131956. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131956. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38692526 Review.
-
Revolutionizing wastewater treatment: A review on the role of advanced functional bio-based hydrogels.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Oct;278(Pt 4):135088. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135088. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39197608 Review.
-
Oil palm biomass as an adsorbent for heavy metals.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014;232:61-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-06746-9_3. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24984835 Review.
-
Nanoengineered metal-organic framework for adsorptive and photocatalytic mitigation of pharmaceuticals and pesticide from wastewater.Environ Pollut. 2022 Sep 1;308:119690. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119690. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Environ Pollut. 2022. PMID: 35772620 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging environmentally friendly bio-based nanocomposites for the efficient removal of dyes and micropollutants from wastewater by adsorption: a comprehensive review.RSC Adv. 2024 Jan 17;14(4):2804-2834. doi: 10.1039/d3ra06501d. eCollection 2024 Jan 10. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38234871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Continuous-Flow System for Methylene Blue Removal Using a Green and Cost-Effective Starch Single-Rod Column.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Oct 4;15(19):3989. doi: 10.3390/polym15193989. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37836037 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels Used for Dye Removal.Gels. 2024 Apr 2;10(4):243. doi: 10.3390/gels10040243. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How the Chemical Properties of Polysaccharides Make It Possible to Design Various Types of Organic-Inorganic Composites for Catalytic Applications.Molecules. 2024 Jul 6;29(13):3214. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133214. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric resins containing modified starch as environmentally friendly adsorbents for dyes and metal ions removal from wastewater.Front Chem. 2024 Oct 30;12:1496901. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1496901. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39539391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations The 17 Goals. [(accessed on 29 June 2023)]. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals.
-
- World Health Organization Drinking-Water. [(accessed on 29 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water.
-
- Cai H., Mei Y., Chen J., Wu Z., Lan L., Zhu D. An Analysis of the Relation between Water Pollution and Economic Growth in China by Considering the Contemporaneous Correlation of Water Pollutants. J. Clean. Prod. 2020;276:122783. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122783. - DOI
-
- Ezbakhe F. Addressing Water Pollution as a Means to Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. J. Water Pollut. Control. 2018;1:6.
-
- Deletic A., Wang H. Water Pollution Control for Sustainable Development. Engineering. 2019;5:839–840. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2019.07.013. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

