The Potential Therapeutic Application of Simvastatin for Brain Complications and Mechanisms of Action
- PMID: 37513826
- PMCID: PMC10385015
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16070914
The Potential Therapeutic Application of Simvastatin for Brain Complications and Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
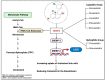
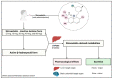
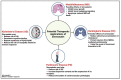
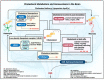
Statins are common drugs that are clinically used to reduce elevated plasma cholesterol levels. Based on their solubility, statins are considered to be either hydrophilic or lipophilic. Amongst them, simvastatin has the highest lipophilicity to facilitate its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Recent studies have suggested that simvastatin could be a promising therapeutic option for different brain complications and diseases ranging from brain tumors (i.e., medulloblastoma and glioblastoma) to neurological disorders (i.e., Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease). Specific mechanisms of disease amelioration, however, are still unclear. Independent studies suggest that simvastatin may reduce the risk of developing certain neurodegenerative disorders. Meanwhile, other studies point towards inducing cell death in brain tumor cell lines. In this review, we outline the potential therapeutic effects of simvastatin on brain complications and review the clinically relevant molecular mechanisms in different cases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; ApoE; CYP46A1; Hh family; Huntington’s disease; LDLR; Parkinson’s disease; cholesterol; lipid rafts; medulloblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cholesterol Hydroxylating Cytochrome P450 46A1: From Mechanisms of Action to Clinical Applications.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jul 8;13:696778. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.696778. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34305573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of CYP46A1 as a novel therapeutic target for neurological disorders: An updated review of mechanisms.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 15;949:175726. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175726. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37062503 Review.
-
CYP46A1 inhibition, brain cholesterol accumulation and neurodegeneration pave the way for Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2015 Aug;138(Pt 8):2383-98. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv166. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Brain. 2015. PMID: 26141492
-
Simvastatin Induces Apoptosis in Medulloblastoma Brain Tumor Cells via Mevalonate Cascade Prenylation Substrates.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 17;11(7):994. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070994. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31319483 Free PMC article.
-
High doses of simvastatin, pravastatin, and cholesterol reduce brain cholesterol synthesis in guinea pigs.Steroids. 2004 Jun;69(6):431-8. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2004.03.012. Steroids. 2004. PMID: 15219793
Cited by
-
Altered Brain Cholesterol Machinery in a Down Syndrome Mouse Model: A Possible Common Feature with Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 3;13(4):435. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040435. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671883 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin, Its Antimicrobial Activity and Its Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 1;12(6):1133. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061133. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Association between Statin Use and Reduced Migraine Likelihood: A Comprehensive Analysis of Migraine Subtypes and Statin Types in a Nationwide Korean Cohort.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 10;17(8):1056. doi: 10.3390/ph17081056. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varolius C., Varolio C. In De Nervis Opticis Nonnullisque Aliis Praeter Communem Opinionem in Humano Capite Observatis: Patavij 1573. Culture et Civilisation, 1969. [(accessed on 1 May 2023)]. Available online: https://books.google.ca/books/about/De_nervis_opticis_nonnullisque_aliis....
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

