New Crystal Form of Human Neuropilin-1 b1 Fragment with Six Electrostatic Mutations Complexed with KDKPPR Peptide Ligand
- PMID: 37513474
- PMCID: PMC10385628
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28145603
New Crystal Form of Human Neuropilin-1 b1 Fragment with Six Electrostatic Mutations Complexed with KDKPPR Peptide Ligand
Abstract
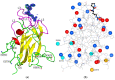
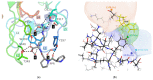
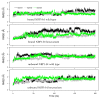
Neuropilin 1 (NRP1), a cell-surface co-receptor of a number of growth factors and other signaling molecules, has long been the focus of attention due to its association with the development and the progression of several types of cancer. For example, the KDKPPR peptide has recently been combined with a photosensitizer and a contrast agent to bind NRP1 for the detection and treatment by photodynamic therapy of glioblastoma, an aggressive brain cancer. The main therapeutic target is a pocket of the fragment b1 of NRP1 (NRP1-b1), in which vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) bind. In the crystal packing of native human NRP1-b1, the VEGF-binding site is obstructed by a crystallographic symmetry neighbor protein, which prevents the binding of ligands. Six charged amino acids located at the protein surface were mutated to allow the protein to form a new crystal packing. The structure of the mutated fragment b1 complexed with the KDKPPR peptide was determined by X-ray crystallography. The variant crystallized in a new crystal form with the VEGF-binding cleft exposed to the solvent and, as expected, filled by the C-terminal moiety of the peptide. The atomic interactions were analyzed using new approaches based on a multipolar electron density model. Among other things, these methods indicated the role played by Asp320 and Glu348 in the electrostatic steering of the ligand in its binding site. Molecular dynamics simulations were carried out to further analyze the peptide binding and motion of the wild-type and mutant proteins. The simulations revealed that specific loops interacting with the peptide exhibited mobility in both the unbound and bound forms.
Keywords: Hirshfeld interface; Neuropilin 1; X-ray crystallography; electrostatic influence; ligand; molecular dynamics simulation; variant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Architecture and hydration of the arginine-binding site of neuropilin-1.FEBS J. 2018 Apr;285(7):1290-1304. doi: 10.1111/febs.14405. Epub 2018 Feb 25. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29430837 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin Fc-Fused Peptide without C-Terminal Arg or Lys Residue Augments Neuropilin-1-Dependent Tumor Vascular Permeability.Mol Pharm. 2018 Feb 5;15(2):394-402. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00761. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29232521
-
Peptides Derived from Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor B Show Potent Binding to Neuropilin-1.Chembiochem. 2022 Jan 5;23(1):e202100463. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100463. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 34647407 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF-A121a binding to Neuropilins - A concept revisited.Cell Adh Migr. 2018 May 4;12(3):204-214. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2017.1372878. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 29095088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropilin-1 enforces extracellular matrix signalling via ABL1 to promote angiogenesis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Oct;42(5):1429-34. doi: 10.1042/BST20140141. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25233427 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical evaluation of 68 Ga-labeled peptide CK2 for PET imaging of NRP-1 expression in vivo.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Jun;51(7):1826-1840. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06632-x. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38319321
-
Endothelial Neuropilin-1: a multifaced signal transducer with an emerging role in inflammation and atherosclerosis beyond angiogenesis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Feb 28;52(1):137-150. doi: 10.1042/BST20230329. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38323651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

