Molecular Regulation of Differential Lipid Molecule Accumulation in the Intramuscular Fat and Abdominal Fat of Chickens
- PMID: 37510361
- PMCID: PMC10379444
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14071457
Molecular Regulation of Differential Lipid Molecule Accumulation in the Intramuscular Fat and Abdominal Fat of Chickens
Abstract
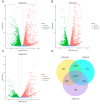
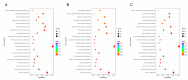
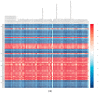
Reducing abdominal fat (AF) accumulation and increasing the level of intramuscular fat (IMF) simultaneously is a major breeding goal in the poultry industry. To explore the different molecular mechanisms underlying AF and IMF, gene expression profiles in the breast muscle (BM) and AF from three chicken breeds were analyzed. A total of 4737 shared DEGs were identified between BM and AF, of which 2602 DEGs were upregulated and 2135 DEGs were downregulated in the BM groups compared with the AF groups. DEGs involved in glycerophospholipid metabolism and glycerolipid metabolism were potential regulators, resulting in the difference in lipid metabolite accumulation between IMF and AF. The PPAR signaling pathway was the most important pathway involved in tissue-specific lipid deposition. Correlation analysis showed that most representative DEGs enriched in the PPAR signaling pathway, such as FABP5, PPARG, ACOX1, and GK2, were negatively correlated with PUFA-enriched glycerophospholipid molecules. Most DEGs related to glycerophospholipid metabolism, such as GPD2, GPD1, PEMT, CRLS1, and GBGT1, were positively correlated with glycerophospholipid molecules, especially DHA- and arachidonic acid (ARA)-containing glycerophospholipid molecules. This study elucidated the molecular mechanism underlying tissue-specific lipid deposition and poultry meat quality.
Keywords: abdominal fat; chicken; glycerophospholipid; integration analysis; intramuscular fat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

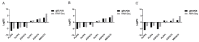


Similar articles
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes and pathways between intramuscular and abdominal fat-derived preadipocyte differentiation of chickens in vitro.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 15;20(1):743. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6116-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31615399 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of intramuscular fat and abdominal fat deposition in chickens.BMC Genomics. 2022 Apr 15;23(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08538-0. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35428174 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes and pathways for intramuscular fat deposition in pectoralis major tissues of fast-and slow-growing chickens.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 30;13:213. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-213. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22646994 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Regulation of Lipogenesis, Adipogenesis and Fat Deposition in Chicken.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 13;12(3):414. doi: 10.3390/genes12030414. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Insights into Molecular Regulation Mechanisms of Intramuscular Fat Deposition in Chicken.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 10;14(12):2197. doi: 10.3390/genes14122197. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38137019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low Testosterone and High Leptin Activate PPAR Signaling to Induce Adipogenesis and Promote Fat Deposition in Caponized Ganders.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 9;25(16):8686. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168686. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201373 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptome and proteome analysis reveals the unique molecular features and nutritional components on the muscles in Chinese Taihe black-bone silky fowl chicken.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 13;19(3):e0299385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299385. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38478538 Free PMC article.
-
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae-Fermented Coconut Water Alleviates Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Enteritis in Wenchang Chicken: A Gut Microbiota and Metabolomic Approach.Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;14(4):575. doi: 10.3390/ani14040575. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396543 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

