Enhancing the Anti-Leukemic Potential of Thymoquinone/Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD) Inclusion Complexes
- PMID: 37509531
- PMCID: PMC10377214
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11071891
Enhancing the Anti-Leukemic Potential of Thymoquinone/Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD) Inclusion Complexes
Abstract
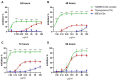
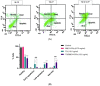
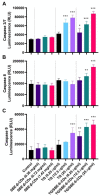
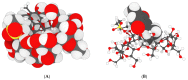
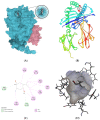
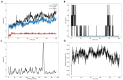
Leukemia, a condition characterized by the abnormal proliferation of blood cells, poses significant challenges in cancer treatment. Thymoquinone (TQ), a bioactive compound derived from black seed, has demonstrated anticancer properties, including telomerase inhibition and the induction of apoptosis. However, TQ's poor solubility and limited bioavailability hinder its clinical application. This study explored the use of Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD), a cyclodextrin derivative, to enhance the solubility and stability of TQ for leukemia treatment. SBE-β-CD offers low hemolytic activity and has been successfully employed in controlled drug release systems. The study investigated the formation of inclusion complexes between TQ and SBE-β-CD and evaluated their effects on leukemia cell growth and telomerase activity. The results indicated that the TQ/SBE-β-CD complex exhibited improved solubility and enhanced cytotoxic effects against K-562 leukemia cells compared to TQ alone, suggesting the potential of SBE-β-CD as a drug delivery system for TQ. The annexin V-FITC assay demonstrated increased apoptosis, while the qPCR quantification assay revealed reduced telomerase activity in leukemia cells treated with TQ/SBE-β-CD, supporting its anti-leukemic potential. The molecular docking analysis indicated a strong binding affinity between TQ and telomerase. However, further research is needed to optimize the apoptotic effects and minimize necrosis induction. In conclusion, TQ/SBE-β-CD shows promise as a novel strategy for leukemia treatment by inhibiting telomerase and enhancing the cytotoxic effects of TQ, offering a potential solution to overcome the limitations of TQ's poor solubility and bioavailability.
Keywords: SBE-β-CD; apoptosis; drug delivery system; leukemia; telomerase inhibition; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
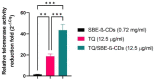

Similar articles
-
Characterization of Thymoquinone-Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex for Anticancer Applications.Molecules. 2023 May 15;28(10):4096. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104096. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241838 Free PMC article.
-
Application of sodium sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin based on encapsulation.Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Jun 1;333:121985. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.121985. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Carbohydr Polym. 2024. PMID: 38494236 Review.
-
Preparation, optimization of the inclusion complex of glaucocalyxin A with sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin and antitumor study.Drug Deliv. 2019 Dec;26(1):309-317. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2019.1568623. Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30896265 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin: A functional biopolymer for drug delivery applications.Carbohydr Polym. 2023 Feb 1;301(Pt B):120347. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120347. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Carbohydr Polym. 2023. PMID: 36446486 Review.
-
Fabrication of sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin/glabridin inclusion complex for promoting bioactivities.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2024 Aug;357(8):e2400082. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202400082. Epub 2024 May 9. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2024. PMID: 38724255
Cited by
-
Flow cytometry-based quantitative analysis of cellular protein expression in apoptosis subpopulations: A protocol.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 25;10(13):e33665. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33665. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39040270 Free PMC article.
-
Folate-Appended Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Induces Autophagic Cell Death in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 24;24(23):16720. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316720. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069042 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

