Girdin regulates both migration and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer cell lines
- PMID: 37503752
- PMCID: PMC10398027
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2023.8606
Girdin regulates both migration and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer cell lines
Abstract
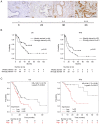
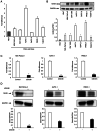
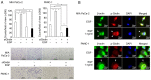
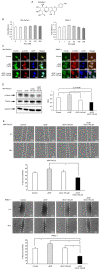
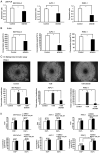
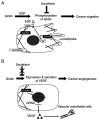
Girdin, an actin‑binding protein, is reportedly involved in the invasion and angiogenesis of various cancers. It has been suggested that the flavonoid Scutellarin (SCU) inhibits Girdin signaling. In the present study, the function and therapeutic applications of Girdin in pancreatic cancer (PaCa) were investigated. Immunohistochemical staining of Girdin in resected PaCa specimens from the Department of Gastroenterological Surgery, Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Science showed that high Girdin expression was associated with poor overall survival and relapse‑free survival, as well as with T factor, indicating invasion into the surrounding tissues. On the other hand, Girdin was highly expressed in almost all PaCa cell lines, and the migration ability of Girdin‑knockdown cell lines was decreased even under epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation. In addition, SCU suppressed PaCa cell migration by inhibiting the phosphorylation of Girdin. The expression and production of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF‑A) was significantly decreased in Girdin‑knockdown cell lines. Furthermore, in Matrigel tube formation assays performed using culture supernatant, the lumen‑forming ability of vascular endothelial cells was also decreased in Girdin‑knockdown cell lines. However, SCU treatment did not significantly alter the expression or production of VEGF‑A. These results suggested that Girdin is involved in EGF signaling‑mediated migration of PaCa cells, that SCU inhibits PaCa invasion by suppressing Girdin activity, and that Girdin is also involved in angiogenesis via an activation pathway different from the action site of SCU. Girdin may be a prognostic biomarker, and the development of a novel molecular‑targeted drugs for Girdin may improve the prognosis of PaCa in the future.
Keywords: cancer angiogenesis; cancer migration; girdin; pancreatic cancer; scutellarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Girdin interaction with vimentin induces EMT and promotes the growth and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2020 Aug;44(2):637-649. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7615. Epub 2020 May 19. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32467989 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic study of Girdin on cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis in different breast cancer subtypes.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Sep;16(3):3351-3356. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6971. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28713924
-
Girdin, a regulator of cell motility, is a potential prognostic marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2013 Jun;29(6):2127-32. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2406. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23588413
-
Girdin, a novel actin-binding protein, and its family of proteins possess versatile functions in the Akt and Wnt signaling pathways.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Nov;1086:169-84. doi: 10.1196/annals.1377.016. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17185515 Review.
-
Girding for migratory cues: roles of the Akt substrate Girdin in cancer progression and angiogenesis.Cancer Sci. 2010 Apr;101(4):836-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01487.x. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20132219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current advances on the therapeutic potential of scutellarin: an updated review.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024 Mar 4;14(1):20. doi: 10.1007/s13659-024-00441-3. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024. PMID: 38436812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rare cause of epileptic encephalopathy: case report of a novel patient with PEHO-like phenotype and CCDC88A gene pathogenic variants.Ital J Pediatr. 2024 Sep 27;50(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13052-024-01766-y. Ital J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39334473 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

