The effects of hesperidin supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in adults: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis
- PMID: 37502716
- PMCID: PMC10369082
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1177708
The effects of hesperidin supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in adults: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis
Abstract
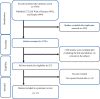
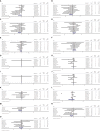
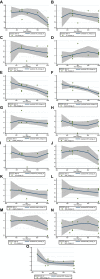
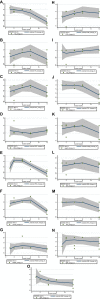
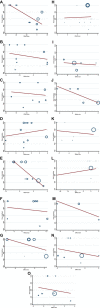
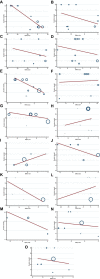
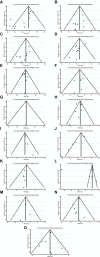
Hesperidin is a naturally occurring bioactive compound that may have an impact on cardiovascular disease risks, but the evidence is not conclusive. To investigate further, this study aimed to explore the effects of hesperidin supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in adults. A comprehensive search was conducted up to August 2022 using relevant keywords in databases such as Scopus, PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and ISI Web of Science for all randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The results showed that hesperidin supplementation had a significant effect on reducing serum triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density cholesterol (LDL), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and systolic blood pressure (SBP), whereas weight was increased. However, no significant effect was observed on high-density cholesterol (HDL), waist circumference (WC), fasting blood glucose (FBG), insulin, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), body mass index (BMI), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP). The study also found that an effective dosage of hesperidin supplementation was around 1,000 mg/d, and a more effective duration of supplementation was more than eight weeks to decrease insulin levels. Furthermore, the duration of intervention of more than six weeks was effective in decreasing FBG levels.
Keywords: adults; blood pressure; body mass index; fasting blood glucose; hesperidin; lipid profile; meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2023 Khorasanian, Fateh, Gholami, Rasaei, Gerami, Khayyatzadeh, Shiraseb and Asbaghi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Hesperidin Supplementation on Cardiometabolic Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Nutr Rev. 2024 Jul 22:nuae084. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuae084. Online ahead of print. Nutr Rev. 2024. PMID: 39038797
-
The effects of saffron supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in adults: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Dec 8;9:1055517. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1055517. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36570145 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of phytosterols on cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Phytother Res. 2025 Jan;39(1):3-24. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8308. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Phytother Res. 2025. PMID: 39572895 Review.
-
The Effects of Nano-Curcumin Supplementation on Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 24;10(7):1015. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071015. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of medical plants from Zingiberaceae family on cardiovascular risk factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Food Biochem. 2022 Jul;46(7):e14130. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14130. Epub 2022 Mar 25. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35332564 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory effect of trans-tiliroside on very low-density lipoprotein secretion in HepG2 cells and mouse liver.J Nat Med. 2024 Jan;78(1):180-190. doi: 10.1007/s11418-023-01756-0. Epub 2023 Nov 16. J Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 37973705 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperidin, a Potential Antiviral Agent against SARS-CoV-2: The Influence of Citrus Consumption on COVID-19 Incidence and Severity in China.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 May 28;60(6):892. doi: 10.3390/medicina60060892. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38929512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Syndrome following Twelve Weeks of Citrus Bioflavonoid Hesperidin Supplementation: A Dose-Response Study.Biomolecules. 2024 May 29;14(6):637. doi: 10.3390/biom14060637. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38927040 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro evaluation of PLGA loaded hesperidin on colorectal cancer cell lines: an insight into nano delivery system.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 2;24(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00882-1. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39095760 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the power of Arctium lappa root: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic applications.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s13659-024-00466-8. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024. PMID: 39162715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . A global brief on hypertension: Silent killer, global public health crisis: World health day 2013. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2013).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

