Zinc-nanoparticles alleviate the ovarian damage induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in pregnant rats and their fetuses
- PMID: 37495867
- PMCID: PMC10624724
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-023-02222-4
Zinc-nanoparticles alleviate the ovarian damage induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in pregnant rats and their fetuses
Abstract
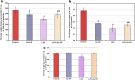
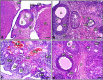
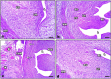
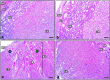
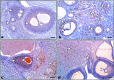
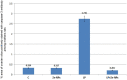
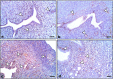
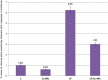
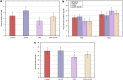
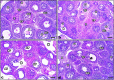
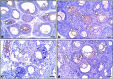
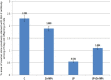
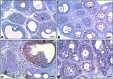
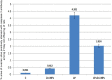
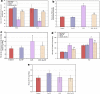
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an endotoxin derived from the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria. LPS exposure during early gestation is associated with adverse effects on the placenta as well as on developmental outcomes, including embryonic resorption, fetal death, congenital teratogenesis, and fetal growth retardation. This work aimed to explore the adverse effects of LPS injected at an early stage of gestation on the gonads of pregnant rats and the ovaries of their pups and the role of zinc nanoparticles (Zn-NPs) against these adverse effects. Twenty-four pregnant rats were used in this study. They were divided at gestation day 4 into four groups (n = 6): control, Zn-NPs (20 mg/kg orally from gestation day E14 till the end of weaning), LPS (50 µg/kg at gestation days E7 and E9), and LPS + Zn-NPs group. The body weight and placenta weight were recorded at gestational day 16. At postnatal day 21 (weaning), the mothers rats and their offspring were sacrificed and immediately dissected to remove the ovaries and uteri from the mothers and the ovaries from their offspring for subsequent biochemical, histological, and immunohistochemical investigations. The obtained results revealed that LPS exposure during early gestation caused severe histopathological alterations in the placenta, uterus, and ovaries of mothers, as well as in the ovaries of their pups. Also, the uterine and ovarian sections displayed a positive reaction for caspase-3 antibody and a negative reaction for Bcl-2 antibody, which reflects the apoptotic effect of LPS. Additionally, remarkable reductions in the levels of antioxidants (superoxide dismutase and catalase) and significant increases in malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were recorded in the serum of LPS-treated mothers and in the ovarian tissues of their offspring. Further biochemical analysis of the ovarian tissues from LPS-maternally treated offspring showed a significant increase in the levels of caspase-3, TNF-α, and TGF-β1, but a significant decrease in the level of IGF-1. On the other hand, treatment of mothers with Zn-NPs from day 14 of gestation until the weaning day (21st day postnatal) successfully ameliorated most of the deleterious histopathological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical changes induced by LPS.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Apoptosis; Gestation; LPS; Ovary; Pups; Zn-NPs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
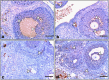
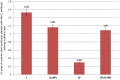
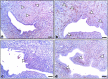
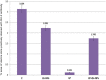
Similar articles
-
Modulatory role of Coriandrum sativum (coriander) extract against diabetic complications on the gonads of female rats and their offspring.Tissue Cell. 2023 Aug;83:102127. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102127. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Tissue Cell. 2023. PMID: 37331322
-
Maternal LPS exposure during pregnancy impairs testicular development, steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in male offspring.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 25;9(9):e106786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106786. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25255222 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal exposure to lipopolysaccharide results in neurodevelopmental damage that is ameliorated by zinc in mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2012 Feb;26(2):326-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.10.002. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Brain Behav Immun. 2012. PMID: 22024135
-
NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Modified One-Generation Study of Bisphenol AF (CASRN 1478-61-1) Administered in Feed to Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD®) Rats with Prenatal, Reproductive Performance, and Subchronic Assessments in F1 Offspring: DART Report 08 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Sep. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Sep. PMID: 36383702 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
NTP Research Report on the CLARITY-BPA Core Study: A Perinatal and Chronic Extended-Dose-Range Study of Bisphenol A in Rats: Research Report 9 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2018 Sep. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2018 Sep. PMID: 31305969 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for LPS-associated female fertility decline.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Oct;41(10):2739-2758. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03226-2. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024. PMID: 39167249 Review.
-
Beyond defence: Immune architects of ovarian health and disease.Semin Immunopathol. 2024 Aug 12;46(3-4):11. doi: 10.1007/s00281-024-01021-w. Semin Immunopathol. 2024. PMID: 39134914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aboelmaaty A, Omara S, Aly M, Kotp M, Ali A. The antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Thymus vulgaris medicinal plant against Escherichia coli and Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharides. Egypt Pharm J. 2022;21(2):153–166. doi: 10.4103/epj.epj_98_21. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

