Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Delivery into the Brain across the Blood-Brain Barrier
- PMID: 37489365
- PMCID: PMC10366925
- DOI: 10.3390/antib12030043
Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Delivery into the Brain across the Blood-Brain Barrier
Abstract
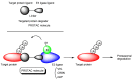
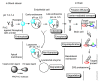
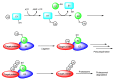
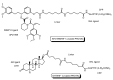
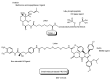
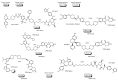
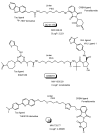
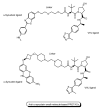
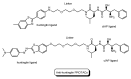
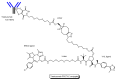
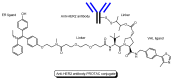
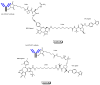
Drug development for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease has challenging difficulties due to the pharmacokinetic impermeability based on the blood-brain barrier (BBB) as well as the blurriness of pharmacodynamic targets based on their unclarified pathogenesis and complicated progression mechanisms. Thus, in order to produce innovative central nervous system (CNS) agents for patients suffering from CNS diseases, effective, selective delivery of CNS agents into the brain across the BBB should be developed. Currently, proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) attract rising attention as a new modality to degrade arbitrary intracellular proteins by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. The internalizations of peptide-based PROTACs by cell-penetrating peptides and that of small molecule-based PROTACs through passive diffusion lack cell selectivity. Therefore, these approaches may bring off-target side effects due to wrong distribution. Furthermore, efflux transporters such as multiple drug resistance 1 (MDR1) expressed at the BBB might interrupt the entry of small molecule-based PROTACs into the brain. Nonetheless, intelligent delivery using machinery systems to absorb the nutrition into the brain for homeostasis, such as carrier-mediated transport (CMT) or receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT), can be established. PROTACs with N-containing groups that are recognized by the proton-coupled organic cation antiporter might cross the BBB through CMT. PROTAC-antibody conjugates (PACs) might cross the BBB through RMT. Subsequently, such small molecule-based PROTACs released in the brain interstitial fluid would be transported into cells such as neurons through passive diffusion and then demonstrate arbitrary protein degradation. In this review, I introduce the potential and advantages of PROTAC delivery into the brain across the BBB through CMT or RMT using PACs in a non-invasive way.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; NanoPROTAC; PROTAC; PROTAC-antibody conjugate; carrier-mediated transport; drug delivery into the brain; receptor-mediated transcytosis; tau protein degradation; the BBB; ubiquitin proteasome system.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Smart Strategies for Therapeutic Agent Delivery into Brain across the Blood-Brain Barrier Using Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2020;68(4):316-325. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c19-00854. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2020. PMID: 32238649 Review.
-
Powering up targeted protein degradation through active and passive tumour-targeting strategies: Current and future scopes.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Nov;263:108725. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108725. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39322067 Review.
-
Brain Cancer Chemotherapy through a Delivery System across the Blood-Brain Barrier into the Brain Based on Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis Using Monoclonal Antibody Conjugates.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 5;10(7):1597. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071597. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-PROTACs: state of the art and perspectives.Nanoscale. 2024 Feb 29;16(9):4378-4391. doi: 10.1039/d3nr06059d. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38305466 Review.
-
Research progress of PROTACs for neurodegenerative diseases therapy.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Jun;147:107386. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107386. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38643565 Review.
Cited by
-
Central Nervous System Targeted Protein Degraders.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 25;13(8):1164. doi: 10.3390/biom13081164. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37627229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breaking Bad Proteins-Discovery Approaches and the Road to Clinic for Degraders.Cells. 2024 Mar 26;13(7):578. doi: 10.3390/cells13070578. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring SureChEMBL from a drug discovery perspective.Sci Data. 2024 May 16;11(1):507. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03371-4. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38755219 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

