Single-cell transcriptomics reveals intestinal cell heterogeneity and identifies Ep300 as a potential therapeutic target in mice with acute liver failure
- PMID: 37488127
- PMCID: PMC10366100
- DOI: 10.1038/s41421-023-00578-4
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals intestinal cell heterogeneity and identifies Ep300 as a potential therapeutic target in mice with acute liver failure
Abstract
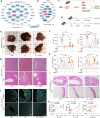
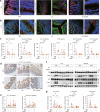
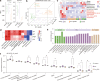
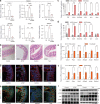
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a severe life-threatening disease associated with the disorder of the gut-liver axis. However, the cellular characteristics of ALF in the gut and related therapeutic targets remain unexplored. Here, we utilized the D-GALN/LPS (D/L)-induced ALF model to characterize 33,216 single-cell transcriptomes and define a mouse ALF intestinal cellular atlas. We found that unique, previously uncharacterized intestinal immune cells, including T cells, B cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, are responsive to ALF, and we identified the transcriptional profiles of these subsets during ALF. We also delineated the heterogeneity of intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) and found that ALF-induced cell cycle arrest in intestinal stem cells and activated specific enterocyte and goblet cell clusters. Notably, the most significantly altered IECs, including enterocytes, intestinal stem cells and goblet cells, had similar activation patterns closely associated with inflammation from intestinal immune activation. Furthermore, our results unveiled a common Ep300-dependent transcriptional program that coordinates IEC activation during ALF, which was confirmed to be universal in different ALF models. Pharmacological inhibition of Ep300 with an inhibitor (SGC-CBP30) inhibited this cell-specific program, confirming that Ep300 is an effective target for alleviating ALF. Mechanistically, Ep300 inhibition restrained inflammation and oxidative stress in the dysregulated cluster of IECs through the P38-JNK pathway and corrected intestinal ecology by regulating intestinal microbial composition and metabolism, thereby protecting IECs and attenuating ALF. These findings confirm that Ep300 is a novel therapeutic target in ALF and pave the way for future pathophysiological studies on ALF.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Acute liver failure is regulated by MYC- and microbiome-dependent programs.Nat Med. 2020 Dec;26(12):1899-1911. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-1102-2. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 33106666
-
Protective Role of 4-Octyl Itaconate in Murine LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Failure via Inhibiting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Aug 17;2021:9932099. doi: 10.1155/2021/9932099. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34457120 Free PMC article.
-
The Qingchangligan Formula Alleviates Acute Liver Failure by Regulating Galactose Metabolism and Gut Microbiota.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 19;11:771483. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.771483. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35127552 Free PMC article.
-
[The protective role of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors-α and pathomechanism in D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide- induced acute liver failure in rats].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Sep;53(9):730-4. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25511408 Chinese.
-
The Key Molecular Mechanisms of Sini Decoction Plus Ginseng Soup to Rescue Acute Liver Failure: Regulating PPARα to Reduce Hepatocyte Necroptosis?J Inflamm Res. 2022 Aug 22;15:4763-4784. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S373903. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36032938 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Identification and Quantification of Basal Endogenous Proteins in the Ileal Digesta of Growing Pigs.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jul 7;14(13):2000. doi: 10.3390/ani14132000. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998112 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

