The intricate mechanism of PLS3 in bone homeostasis and disease
- PMID: 37484945
- PMCID: PMC10361617
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1168306
The intricate mechanism of PLS3 in bone homeostasis and disease
Abstract
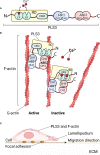
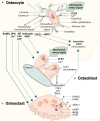
Since our discovery in 2013 that genetic defects in PLS3 lead to bone fragility, the mechanistic details of this process have remained obscure. It has been established that PLS3 variants cause syndromic and nonsyndromic osteoporosis as well as osteoarthritis. PLS3 codes for an actin-bundling protein with a broad pattern of expression. As such, it is puzzling how PLS3 specifically leads to bone-related disease presentation. Our review aims to summarize the current state of knowledge regarding the function of PLS3 in the predominant cell types in the bone tissue, the osteocytes, osteoblasts and osteoclasts. This is related to the role of PLS3 in regulating mechanotransduction, calcium regulation, vesicle trafficking, cell differentiation and mineralization as part of the complex bone pathology presented by PLS3 defects. Considering the consequences of PLS3 defects on multiple aspects of bone tissue metabolism, our review motivates the study of its mechanism in bone diseases which can potentially help in the design of suitable therapy.
Keywords: PLS3; bone cells; bone diseases; calcium regulation; mechanotransduction; osteogenesis.
Copyright © 2023 Zhong, Pathak, Liang, Zhytnik, Pals, Eekhoff, Bravenboer and Micha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PLS3 Deletions Lead to Severe Spinal Osteoporosis and Disturbed Bone Matrix Mineralization.J Bone Miner Res. 2017 Dec;32(12):2394-2404. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3233. Epub 2017 Sep 6. J Bone Miner Res. 2017. PMID: 28777485
-
Plastin 3 influences bone homeostasis through regulation of osteoclast activity.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Dec 15;27(24):4249-4262. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy318. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 30204862
-
The actin-bundling protein, PLS3, is part of the mechanoresponsive machinery that regulates osteoblast mineralization.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 27;11:1141738. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1141738. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38089885 Free PMC article.
-
Plastin 3 in health and disease: a matter of balance.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jul;78(13):5275-5301. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03843-5. Epub 2021 May 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34023917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of autophagy in bone homeostasis.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Jun;236(6):4152-4173. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30111. Epub 2021 Jan 16. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33452680 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Insights in PLS3-Mediated Osteogenic Regulation.Cells. 2024 Sep 9;13(17):1507. doi: 10.3390/cells13171507. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273077 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoporosis: Molecular Pathology, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 26;24(19):14583. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914583. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoporotic Burst Fracture in a Young Male Adult as First Presentation of a Rare PLS3 Mutation: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Dec 29;15(12):e51264. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51264. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38283430 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclast-specific Plastin 3 knockout in mice fail to develop osteoporosis despite dramatic increased osteoclast resorption activity.JBMR Plus. 2024 Jan 4;8(1):ziad009. doi: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziad009. eCollection 2024 Jan. JBMR Plus. 2024. PMID: 38549711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hagiwara M, Shinomiya H, Kashihara M, Kobayashi K, Tadokoro T, Yamamoto Y. Interaction of activated Rab5 with actin-bundling proteins, l- and T-plastin and its relevance to endocytic functions in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (2011) 407(3):615–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.082 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ikeda H, Sasaki Y, Kobayashi T, Suzuki H, Mita H, Toyota M, et al. . The role of T-fimbrin in the response to DNA damage: silencing of T-fimbrin by small interfering rna sensitizes human liver cancer cells to DNA-damaging agents. Int J Oncol (2005) 27(4):933–40. doi: 10.3892/ijo.27.4.933 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

