Retinal gliosis and phenotypic diversity of intermediate filament induction and remodeling upon acoustic blast overpressure (ABO) exposure to the rat eye
- PMID: 37481225
- PMCID: PMC10730083
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2023.109585
Retinal gliosis and phenotypic diversity of intermediate filament induction and remodeling upon acoustic blast overpressure (ABO) exposure to the rat eye
Abstract
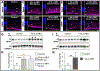
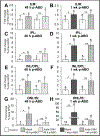
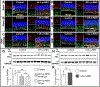
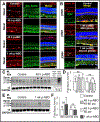
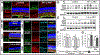
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by acoustic blast overpressure (ABO) is frequently associated with chronic visual deficits in military personnel and civilians. In this study, we characterized retinal gliotic response in adult male rats following a single ABO exposure directed to one side of the head. Expression of gliosis markers and intermediate filaments was assessed at 48 h and 1 wk post-ABO exposure, in comparison to age-matched non-exposed control retina. In response to a single ABO exposure, type III IF, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was variably induced in a subpopulation of retinal Müller glia in ipsilateral eyes. ABO-exposed eyes exhibited radial Müller glial GFAP filament extension through the inner plexiform layer (IPL) and the inner nuclear layer (INL) through the retina in both the nasal quadrant and juxta-optic nerve head (jONH) eye regions at 1 wk post-ABO. We observed an ∼6-fold increase (p ≤ 0.05) in radial glial GFAP immunolabeling in the IPL in both eye regions, in comparison to regionally matched controls. Similarly, GFAP extension through the INL into the outer retina was elevated ∼3-fold, p ≤ 0.05 in the nasal retina, but exhibited wider variability in the jONH retina. In contrast, constitutive type III IF vimentin exhibited greater remodeling in retinal Müller glia through the jONH retina compared to the nasal retina in response to ABO. We observed areas of lateral vimentin remodeling through the Müller glial end-feet, and greater mid-outer retinal radial vimentin IF extension in a subpopulation of glia at 1 wk post-ABO. We also observed a significant increase in total retinal levels of the type III IF desmin in ABO-exposed retina vs. controls (∼1.6-fold, p ≤ 0.01). In addition, ABO-exposure elicited varied glial induction of developmentally regulated type VI family IFs (nestin and synemin) in subpopulations of Müller cells at 48 h and 1 wk post-ABO. We demonstrate that multiple glial phenotypes emerge in the rat retina following a single ABO exposure, rather than a global homogeneous retinal glial response, involving less well characterized IF protein forms which warrant further investigation in the context of ABO-induced retinal gliosis.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Citrullination of glial intermediate filaments is an early response in retinal injury.Mol Vis. 2016 Sep 26;22:1137-1155. eCollection 2016. Mol Vis. 2016. PMID: 27703308 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiles of nestin and synemin in reactive astrocytes and Müller cells following retinal injury: a comparison with glial fibrillar acidic protein and vimentin.Mol Vis. 2010 Nov 27;16:2511-23. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 21139996 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-mediated suppression of vimentin or glial fibrillary acidic protein prevents the establishment of Müller glial cell hypertrophy in progressive retinal degeneration.Glia. 2021 Sep;69(9):2272-2290. doi: 10.1002/glia.24034. Epub 2021 May 24. Glia. 2021. PMID: 34029407
-
Up-regulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein in response to retinal injury: its potential role in glial remodeling and a comparison to vimentin expression.Int Rev Cytol. 2003;230:263-90. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(03)30005-1. Int Rev Cytol. 2003. PMID: 14692684 Review.
-
Type III Intermediate Filaments Desmin, Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP), Vimentin, and Peripherin.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 Dec 1;9(12):a021642. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021642. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017. PMID: 29196434 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blast injury: Impact to the cornea.Exp Eye Res. 2024 Jul;244:109915. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2024.109915. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Exp Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38677709 Review.
-
IC100, a humanized therapeutic monoclonal anti-ASC antibody alleviates oxygen-induced retinopathy in mice.Angiogenesis. 2024 Aug;27(3):423-440. doi: 10.1007/s10456-024-09917-9. Epub 2024 May 6. Angiogenesis. 2024. PMID: 38709389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agnetti G, Herrmann H, Cohen S, 2022. New roles for desmin in the maintenance of muscle homeostasis. FEBS J 289, 2755–2770. - PubMed
-
- Allen RS, Motz CT, Singh A, Feola A, Hutson L, Douglass A, Ramachandra Rao S, Skelton LA, Cardelle L, Bales KL, Chesler K, Gudapati K, Ethier CR, Harper MM, Fliesler SJ, Pardue MT, 2021. Dependence of visual and cognitive outcomes on animal holder configuration in a rodent model of blast overpressure exposure. Vis. Res 188, 162–173. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellin RM, Huiatt TW, Critchley DR, Robson RM, 2001. Synemin may function to directly link muscle cell intermediate filaments to both myofibrillar Z-lines and costameres. J. Biol. Chem 276, 32330–32337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

