Knockdown of ELF4 aggravates renal injury in ischemia/reperfusion mice through promotion of pyroptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 37474923
- PMCID: PMC10360327
- DOI: 10.1186/s12860-023-00485-2
Knockdown of ELF4 aggravates renal injury in ischemia/reperfusion mice through promotion of pyroptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
Background: Renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is a major cause of acute kidney injury (AKI). Dysfunction of E74-like ETS transcription factor 4 (ELF4) leads to inflammation. This research intended to look into the function and mechanisms of ELF4 in I/R and oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) model.
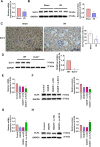
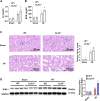
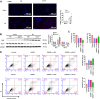
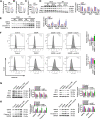
Results: In I/R and OGD/R model, ELF4 expression was downregulated. ELF4 knockout aggravated I/R-induced kidney injury, oxidative stress (OS), endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), apoptosis, inflammation, and pyroptosis in mice. In HK-2 cells treated with OGD/R, suppression of ELF4 expression inhibited cell proliferation and promoted cell apoptosis, OS, ERS, inflammation, and pyroptosis. Moreover, ELF4 overexpression led to the opposite results.
Conclusion: ELF4 deficiency aggravated I/R induced AKI, which was involved in apoptosis, OS, ERS, inflammation, and pyroptosis. Targeting ELF4 may be a promising new therapeutic strategy for preventing inflammation after IR-AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; ELF4; Inflammation; Oxidative stress; Pyroptosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute kidney injury: exploring endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 12;15:1308733. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1308733. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38434710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gypenoside XVII attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and NLRP3 inflammasome-triggered pyroptosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 5;962:176187. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176187. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37984729
-
Connexin32 plays a crucial role in ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis signaling pathway in ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.J Transl Med. 2018 May 4;16(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1493-8. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29728112 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT3 mediates mitofusin 2 ubiquitination and degradation to suppress ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Nov 15;408(2):112861. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112861. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34624325
-
Pyroptosis: The Determinator of Cell Death and Fate in Acute Kidney Injury.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2023 Dec 22;10(2):118-131. doi: 10.1159/000535894. eCollection 2024 Apr. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38751798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Astragaloside IV Alleviates Podocyte Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy through Regulating IRE-1α/NF-κ B/NLRP3 Pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Jul 23. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3568-0. Online ahead of print. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 39039342
-
Acute kidney injury: exploring endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 12;15:1308733. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1308733. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38434710 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jun W, Benjanuwattra J, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N. Necroptosis in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: A major mode of cell death? Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;689(108433):26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

