Integrative analysis of genes reveals endoplasmic reticulum stress-related immune responses involved in dilated cardiomyopathy with fibrosis
- PMID: 37462883
- PMCID: PMC10425499
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-023-01871-z
Integrative analysis of genes reveals endoplasmic reticulum stress-related immune responses involved in dilated cardiomyopathy with fibrosis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Integrative analysis of genes reveals endoplasmic reticulum stress-related immune responses involved in dilated cardiomyopathy with fibrosis.Apoptosis. 2023 Oct;28(9-10):1422. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01881-x. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 37561243 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
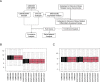
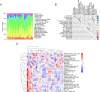
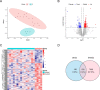
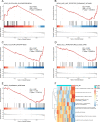
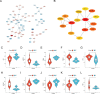
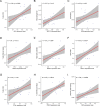
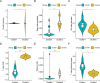
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been implicated in the mechanisms underlying the fibrotic process in dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and results in disease exacerbation; however, the molecular details of this mechanism remain unclear. Through microarray and bioinformatic analyses, we explored genetic alterations in myocardial fibrosis (MF) and identified potential biomarkers related to ER stress. We integrated two public microarray datasets, including 19 DCM and 16 control samples, and comprehensively analyzed differential expression, biological functions, molecular interactions, and immune infiltration levels. The immune cell signatures suggest that inflammatory immune imbalance may promote MF progression. Both innate and adaptive immunity are involved in MF development, and T-cell subsets account for a considerable proportion of immune infiltration. The immune subtypes were further compared, and 103 differentially expressed ER stress-related genes were identified. These genes were mainly enriched in neuronal apoptosis, protein modification, oxidative stress reaction, glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, and NOD-like receptor signaling pathways. Furthermore, the 15 highest-scoring core genes were identified. Seven hub genes (AK1, ARPC3, GSN, KPNA2, PARP1, PFKL, and PRKC) might participate in immune-related mechanisms. Our results offer a new integrative view of the pathways and interaction networks of ER stress-related genes and provide guidance for developing novel therapeutic strategies for MF.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Dilated cardiomyopathy; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Immune cells; Myocardial fibrosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of Target Genes and Transcription Factors in Mice with LMNA-Related Dilated Cardiomyopathy by Integrated Bioinformatic Analyses.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jun 14;26:e924576. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924576. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32581210 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the pathogenesis and immune infiltration in dilated cardiomyopathy complicated with atrial fibrillation by bioinformatics analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 17;14:1049351. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1049351. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36733486 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-related gene expression causes the progression of dilated cardiomyopathy by inducing apoptosis.Front Genet. 2024 Apr 18;15:1366087. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1366087. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38699233 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Dilated Cardiomyopathy: New Insights for an Old Entity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 5;23(21):13573. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113573. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMI).Herz. 2005 Sep;30(6):535-44. doi: 10.1007/s00059-005-2730-5. Herz. 2005. PMID: 16170686 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning-based derivation and validation of three immune phenotypes for risk stratification and prognosis in community-acquired pneumonia: a retrospective cohort study.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 24;15:1441838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1441838. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39114653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han M, Zhou B (2022) Role of cardiac fibroblasts in Cardiac Injury and Repair. Curr Cardiol Rep - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

