Novel complete methanogenic pathways in longitudinal genomic study of monogastric age-associated archaea
- PMID: 37461084
- PMCID: PMC10353118
- DOI: 10.1186/s42523-023-00256-6
Novel complete methanogenic pathways in longitudinal genomic study of monogastric age-associated archaea
Abstract
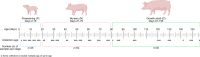
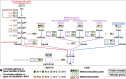
Background: Archaea perform critical roles in the microbiome system, including utilizing hydrogen to allow for enhanced microbiome member growth and influencing overall host health. With the majority of microbiome research focusing on bacteria, the functions of archaea are largely still under investigation. Understanding methanogenic functions during the host lifetime will add to the limited knowledge on archaeal influence on gut and host health. In our study, we determined lifelong archaea dynamics, including detection and methanogenic functions, while assessing global, temporal and host distribution of our novel archaeal metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs). We followed 7 monogastric swine throughout their life, from birth to adult (1-156 days of age), and collected feces at 22 time points. The samples underwent gDNA extraction, Illumina sequencing, bioinformatic quality and assembly processes, MAG taxonomic assignment and functional annotation. MAGs were utilized in downstream phylogenetic analysis for global, temporal and host distribution in addition to methanogenic functional potential determination.
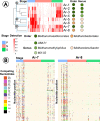
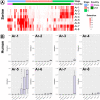
Results: We generated 1130 non-redundant MAGs, representing 588 unique taxa at the species level, with 8 classified as methanogenic archaea. The taxonomic classifications were as follows: orders Methanomassiliicoccales (5) and Methanobacteriales (3); genera UBA71 (3), Methanomethylophilus (1), MX-02 (1), and Methanobrevibacter (3). We recovered the first US swine Methanobrevibacter UBA71 sp006954425 and Methanobrevibacter gottschalkii MAGs. The Methanobacteriales MAGs were identified primarily during the young, preweaned host whereas Methanomassiliicoccales primarily in the adult host. Moreover, we identified our methanogens in metagenomic sequences from Chinese swine, US adult humans, Mexican adult humans, Swedish adult humans, and paleontological humans, indicating that methanogens span different hosts, geography and time. We determined complete metabolic pathways for all three methanogenic pathways: hydrogenotrophic, methylotrophic, and acetoclastic. This study provided the first evidence of acetoclastic methanogenesis in archaea of monogastric hosts which indicated a previously unknown capability for acetate utilization in methanogenesis for monogastric methanogens. Overall, we hypothesized that the age-associated detection patterns were due to differential substrate availability via the host diet and microbial metabolism, and that these methanogenic functions are likely crucial to methanogens across hosts. This study provided a comprehensive, genome-centric investigation of monogastric-associated methanogens which will further improve our understanding of microbiome development and functions.
Keywords: Archaea; Methanogenesis; Microbiome; Monogastric; Swine.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tracking investigation of archaeal composition and methanogenesis function from parental to offspring pigs.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Jun 1;927:172078. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172078. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38582109
-
Methylotrophy in the Mire: direct and indirect routes for methane production in thawing permafrost.mSystems. 2024 Jan 23;9(1):e0069823. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00698-23. Epub 2023 Dec 8. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38063415 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse and unconventional methanogens, methanotrophs, and methylotrophs in metagenome-assembled genomes from subsurface sediments of the Slate River floodplain, Crested Butte, CO, USA.mSystems. 2024 Jul 23;9(7):e0031424. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00314-24. Epub 2024 Jun 28. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38940520 Free PMC article.
-
Methylotrophic methanogens everywhere - physiology and ecology of novel players in global methane cycling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Dec 20;47(6):1895-1907. doi: 10.1042/BST20180565. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31819955 Review.
-
Metagenome, metatranscriptome, and metaproteome approaches unraveled compositions and functional relationships of microbial communities residing in biogas plants.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jun;102(12):5045-5063. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8976-7. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29713790 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A metagenomic catalogue of the ruminant gut archaeome.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 7;15(1):9609. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54025-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39505912 Free PMC article.
-
The role of gut archaea in the pig gut microbiome: a mini-review.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 9;14:1284603. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1284603. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37876779 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nkamga VD, Henrissat B, Drancourt M. Archaea: essential inhabitants of the human digestive microbiota. Human Microbiome Journal. 2017;3:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.humic.2016.11.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
