Antibiofilm and antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus cell free supernatant against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn wounds
- PMID: 37455022
- PMCID: PMC10681627
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.14305
Antibiofilm and antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus cell free supernatant against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn wounds
Abstract
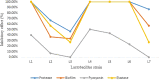
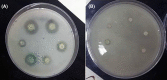
The present study investigated the antimicrobial and anti-biofilm effects of indigenous Lactobacillus probiotic strains on Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn wound infection in laboratory conditions. The effect of 7 probiotic strains isolated from infant faeces on the pathogenicity factors of P. aeruginosa, including protease, elastase, antibiofilm and antipyocyanin was measured. Also, diffusion methods in the well and micro broth dilution were used to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of probiotics. All tests were performed in triplicate. A negative control and a positive control were used for each test. SPSS version 22 software was used for statistical analysis, and a p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. A total of 30 clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa were isolated. The elastolytic activity of P. aeruginosa isolates decreased after adding Cell free supernatant (CFS) of each Lactobacillus. L1, L4, L5, and L6 strains had a 100% inhibitory effect on pathogen isolates. L3 and L7 strains had the lowest inhibitory effect. The inhibitory effect of CFS extracted from lactobacilli on protease production by P. aeruginosa. L1, L4, L5, and L6 strains had an inhibitory effect on all tested isolates. L2, L3, and L7 strains had a less inhibitory effect. L4 strain had the highest inhibitory effect on pyocyanin production by P. aeruginosa (50%), followed by L5 (43.3%), L1 (40%), and L6 (23.3%) strains. L3 and L7 strains had no inhibitory effect on the pyocyanin production of P. aeruginosa isolates. It was found that the CFS of 4 isolates (L1, L4, L5, and L6) was the most active extract and had a 100% inhibitory effect against biofilm formation of all P. aeruginosa strains. The L3 strain had the least inhibitory effect against the biofilm formation of pathogens. Overall, this study showed that probiotics could be promising alternatives to combat the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa in burn wounds.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; burns; probiotics; wounds and injuries.
© 2023 The Authors. International Wound Journal published by Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell-free supernatants from Lactobacillus strains exert antibacterial, antibiofilm, and antivirulence activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients.Microbes Infect. 2024 May-Jun;26(4):105301. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2024.105301. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38237656
-
In vitro and in vivo antibiofilm activity of the synthetic antimicrobial peptide WLBU2 against multiple drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.BMC Microbiol. 2023 May 15;23(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02886-x. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37183241 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Chitosan Scaffold Loaded with Soluble Factors of Different Probiotic Strains Against Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Iran J Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 1;22(1):e3612. doi: 10.30498/ijb.2024.381455.3612. eCollection 2024 Jan. Iran J Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38827340 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Antagonistic Effect of Indigenous Probiotics on Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Sep 28;2023:6645657. doi: 10.1155/2023/6645657. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37810624 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Among Antibiotic Resistance, Biofilm Formation and lasB Gene in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated from Burn Patients.Clin Lab. 2018 Sep 1;64(9):1477-1484. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2018.180331. Clin Lab. 2018. PMID: 30274028
Cited by
-
Vibriocidal efficacy of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus acidophilus cell-free supernatants encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles against multi-drug resistant Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):905. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09810-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39223499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mobayen M, Pour‐Abbas SE, Naghipour M, Akhoundi M, Ashoobi MT. Evaluating the knowledge and attitudes of the members of the medical community mobilization on first aid for burn injuries in Guilan, Iran. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. 2020;30(186):148‐155.
-
- Feizkhah A, Mobayen M, Habibiroudkenar P, et al. The importance of considering biomechanical properties in skin graft: are we missing something? Burns. 2022;48(7):1768‐1769. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical