Biochemical Changes Induced by the Administration of Cannabis sativa Seeds in Diabetic Wistar Rats
- PMID: 37447270
- PMCID: PMC10346897
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15132944
Biochemical Changes Induced by the Administration of Cannabis sativa Seeds in Diabetic Wistar Rats
Abstract
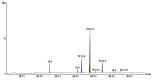
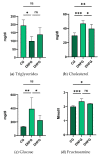
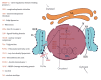
The present pilot study investigates the blood biochemical changes induced by hemp seeds in rats with diabetes. The composition of industrial hemp seeds, antioxidant activity, identification and quantification of phenols and fatty acids from hemp oil were determined. The Wistar adult rats used in the experiment were divided into three groups (n = 6) and kept under standard conditions. Group one, the control group (individuals without diabetes), and group two (diabetic individuals) received water and normal food ad libitum, while the third group, also including diabetic individuals, received specific food (hemp seeds) and water ad libitum. Subsequent blood biochemical parameters were determined. Hemp seeds had higher phenol (14 compounds), flavonoids and PUFA contents compared to other plants seeds. In addition, the antioxidant activity in Cannabis sativa was also increased. Moreover, the ratio between n-6 and n-3 was 4.41, ideal for different diseases. Additionally, all biochemical parameters showed significant changes following the treatment. It was shown that high doses of hemp seeds decreased diabetes-induced biochemical damage in rats most probably due to the high content of active compounds. In order to use these seeds in humans, it is essential to find out which hemp compounds are particularly responsible for these effects. Moreover, for the objective investigation of their effects, longer-term studies are needed.
Keywords: cannabis; fatty acids; glycemia; hydroxybenzoic acid; phenolic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparing the extraction methods, chemical composition, phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of edible oils from Cannabis sativa and Silybum marianu seeds.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 29;12(1):20609. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25030-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36446937 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seeds and Hemp Seed Oil on Vascular Dysfunction in Obese Male Zucker Rats.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 27;13(8):2575. doi: 10.3390/nu13082575. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444734 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil press-cake and decaffeinated green tea leaves (Camellia sinensis) on functional characteristics of gluten-free crackers.J Food Sci. 2014 Mar;79(3):C318-25. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12370. Epub 2014 Feb 13. J Food Sci. 2014. PMID: 24527987
-
Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.) as a Valuable Source of Natural Ingredients for Functional Foods-A Review.Molecules. 2024 May 1;29(9):2097. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092097. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa subsp. sativa) as an Emerging Source for Value-Added Functional Food Ingredients and Nutraceuticals.Molecules. 2020 Sep 7;25(18):4078. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184078. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32906622 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chinese Sumac Fruits (Rhus chinesis Mill.) Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes in C57BL/6 Mice through Repairing Islet Cell Functions, Regulating IRS-1/PI3K/AKT Pathways and Promoting the Entry of Nrf2 into the Nucleus.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 21;15(18):4080. doi: 10.3390/nu15184080. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764863 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Adding Hempseed Cake on Sperm Traits, Body Weight, Haematological and Biochemical Parameters in Rabbit Males.Vet Sci. 2024 Oct 16;11(10):509. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11100509. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39453101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Majewski M.K., Ognik K., Juśkiewicz J. The antioxidant status, lipid profile, and modulation of vascular function by fish oil supplementation in nano-copper and copper carbonate fed Wistar rats. J. Funct. Foods. 2020;64:103595. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103595. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

