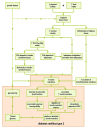
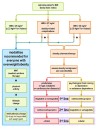
Diagnosis and Non-Invasive Treatment of Obesity in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Guidelines
- PMID: 37445466
- PMCID: PMC10342979
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12134431
Diagnosis and Non-Invasive Treatment of Obesity in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Guidelines
Abstract
Obesity, a chronic disease with multifactorial etiopathogenesis, is characterized by excessive accumulation of adipose tissue. Obesity prevalence is growing globally at an alarming rate. The overwhelming majority of obesity cases are caused by inappropriate lifestyles, such as overconsumption of food and inadequate physical activity. Metabolic and biochemical changes due to increased adiposity resulted in numerous comorbidities, increased all-cause mortality, and reduced quality of life. T2DM (type 2 diabetes mellitus) and obesity have many common pathogenetic points and drive each other in a vicious cycle. The aim of this article is to review obesity management guidelines and highlight the most important points. Management of both obesity-related and T2DM complications incur enormous expenses on healthcare systems. It is, therefore, paramount to provide streamlined yet custom-tailored weight management in order to avoid the negative ramifications of both diseases. Efficient obesity treatment leads to better diabetes control since some antidiabetic medications support weight reduction. Obesity treatment should be overseen by a multi-disciplinary team providing indispensable information and individually tailored regimens to patients. Weight management should be multimodal and consist chiefly of MNT (medical nutrition therapy), physical activity, and lifestyle changes. A comprehensive approach to obesity treatment may give tangible results to quality of life and comorbidities.
Keywords: GLP1-RA; SLGT2 inhibitor; medical nutrition therapy; weight management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effectiveness of web-based programs on the reduction of childhood obesity in school-aged children: A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-14. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-248. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820152
-
[Pharmacological therapy of obesity].G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008 Apr;9(4 Suppl 1):83S-93S. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008. PMID: 18773755 Italian.
-
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS AND AMERICAN COLLEGE OF ENDOCRINOLOGY COMPREHENSIVE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MEDICAL CARE OF PATIENTS WITH OBESITY.Endocr Pract. 2016 Jul;22 Suppl 3:1-203. doi: 10.4158/EP161365.GL. Epub 2016 May 24. Endocr Pract. 2016. PMID: 27219496
-
Treatment modalities of obesity: what fits whom?Diabetes Care. 2008 Feb;31 Suppl 2:S269-77. doi: 10.2337/dc08-s265. Diabetes Care. 2008. PMID: 18227496 Review.
-
Oral antidiabetic agents: current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Drugs. 2005;65(3):385-411. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565030-00005. Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15669880 Review.
Cited by
-
Modern Management of Cardiometabolic Continuum: From Overweight/Obesity to Prediabetes/Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Recommendations from the Eastern and Southern Europe Diabetes and Obesity Expert Group.Diabetes Ther. 2024 Sep;15(9):1865-1892. doi: 10.1007/s13300-024-01615-5. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Diabetes Ther. 2024. PMID: 38990471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can Adipokine FAM19A5 Be a Biomarker of Metabolic Disorders?Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Apr 10;17:1651-1666. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S460226. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38616989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory Effects of Isolated Lactobacillus paracasei from Malaysian Water Kefir Grains on the Intestinal Barrier and Gut Microbiota in Diabetic Mice.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Sep 23. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10367-4. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 39313703
-
Association of cardiorespiratory fitness level with vascular function and subclinical atherosclerosis in the elderly.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024 May;124(5):1487-1497. doi: 10.1007/s00421-023-05375-1. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38133663 Free PMC article.
-
Gut-targeted therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Jan 6;12(1):1-8. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i1.1. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38292634 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vettor R., Conci S. Obesity Pathogenesis. In: Sbraccia P., Finer N., editors. Obesity: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. 89–108.
-
- World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight—Fact Sheets. 2020. [(accessed on 9 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) Defining Adult Overweight and Obesity|Overweight & Obesity. [(accessed on 9 May 2023)];2017 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult/defining.html.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources