Moderate exercise-induced dynamics on key sepsis-associated signaling pathways in the liver
- PMID: 37407986
- PMCID: PMC10324277
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-023-04551-1
Moderate exercise-induced dynamics on key sepsis-associated signaling pathways in the liver
Abstract
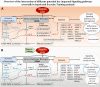
Background: There is a clear relationship between quantitative measures of fitness (e.g., VO2 max) and outcomes after surgical procedures. Whether or not fitness is a modifiable risk factor and what underlying biological processes drive these changes are not known. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the moderate exercise training effect on sepsis outcomes (survival) as well as the hepatic biological response. We chose to study the liver because it plays a central role in the regulation of immune defense during systemic infection and receives blood flow directly from the origin of infection (gut) in the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model.
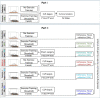
Methods: We randomized 50 male (♂) and female (♀) Sprague-Dawley rats (10 weeks, 340 g) to 3 weeks of treadmill exercise training, performed CLP to induce polymicrobial "sepsis," and monitored survival for five days (Part I). In parallel (Part II), we randomized 60 rats to control/sedentary (G1), exercise (G2), exercise + sham surgery (G3), CLP/sepsis (G4), exercise + CLP [12 h (G5) and 24 h (G6)], euthanized at 12 or 24 h, and explored molecular pathways related to exercise and sepsis survival in hepatic tissue and serum.
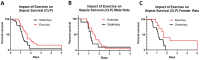
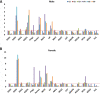
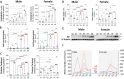
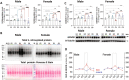
Results: Three weeks of exercise training significantly increased rat survival following CLP (polymicrobial sepsis). CLP increased inflammatory markers (e.g., TNF-a, IL-6), which were attenuated by exercise. Sepsis suppressed the SOD and Nrf2 expression, and exercise before sepsis restored SOD and Nrf2 levels near the baseline. CLP led to increased HIF1a expression and oxidative and nitrosative stress, the latter of which were attenuated by exercise. Haptoglobin expression levels were increased in CLP animals, which was significantly amplified in exercise + CLP (24 h) rats.
Conclusions: Moderate exercise training (3 weeks) increased the survival in rats exposed to CLP, which was associated with less inflammation, less oxidative and nitrosative stress, and activation of antioxidant defense pathways.
Keywords: CLP; Exercise training; Liver injury; Sepsis-hub genes; Sepsis-survival.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Thiele performs consulting work on advanced monitoring technology for Medtronic, Edwards LifeSciences, and Philips Medical. Dr. Thiele received an investigator-initiated award from Apple to explore the use of exercise training in patients undergoing cancer surgery. Dr. Thiele has an NIH Grant (R-21, NIBIB) to develop near-infrared spectroscopy equipment to measure the oxidation state of cytochrome aa3 non-invasively. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Dynamics of hepatic gene expression profile in a rat cecal ligation and puncture model.J Surg Res. 2012 Aug;176(2):583-600. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2011.11.1031. Epub 2011 Dec 15. J Surg Res. 2012. PMID: 22381171 Free PMC article.
-
[Role and mechanism of SIRT1 in regulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in septic liver injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Jun;35(6):598-603. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220815-00744. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37366125 Chinese.
-
[Effect of SIRT1 regulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway on sepsis-induced acute lung injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Mar;35(3):244-249. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220815-00745. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 36916335 Chinese.
-
Astragaloside IV Attenuates Polymicrobial Sepsis-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction in Rats via IKK/NF-κB Pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2021 Nov;27(11):825-831. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-2869-9. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Chin J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 34432200
-
Hydrogen-rich saline ameliorates lung injury associated with cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis in rats.Exp Mol Pathol. 2015 Apr;98(2):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25746665 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteome characterization of liver-kidney comorbidity after microbial sepsis.FASEB J. 2024 Apr 15;38(7):e23597. doi: 10.1096/fj.202302520R. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38581235
-
Impact of Exercise Training on Survival Rate and Neural Cell Death in Sepsis Through the Maintenance of Redox Equilibrium.Int Neurourol J. 2024 Mar;28(1):22-32. doi: 10.5213/inj.2448044.022. Epub 2024 Mar 31. Int Neurourol J. 2024. PMID: 38569617 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and risk of sepsis: a two-sample mendelian randomization study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 19;11:1436546. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1436546. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39224605 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Interferon-Induced Proteins with Tetratricopeptide Repeats 1 and 2 in Sepsis-Induced Acute Liver Injury.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Jun 12;17:2337-2349. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S459838. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38882652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karlsson E, Egenvall M, Farahnak P, Bergenmar M, Nygren-Bonnier M, Franzen E, Rydwik E. Better preoperative physical performance reduces the odds of complication severity and discharge to care facility after abdominal cancer resection in people over the age of 70—a prospective cohort study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44:1760–1767. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.08.011. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

