Friend or foe for obesity: How hepatokines remodel adipose tissues and translational perspective
- PMID: 37396511
- PMCID: PMC10308077
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.12.011
Friend or foe for obesity: How hepatokines remodel adipose tissues and translational perspective
Abstract
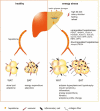
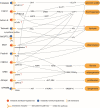
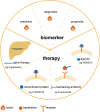
Due to excess energy intake and a sedentary lifestyle, the prevalence of obesity is rising steadily and has emerged as a global public health problem. Adipose tissue undergoes structural remodeling and dysfunction in the obese state. Secreted proteins derived from the liver, also termed as hepatokines, exert multiple effects on adipose tissue remodeling and the development of obesity, and has drawn extensive attention for their therapeutic potential in the treatment of obesity and related diseases. Several novel hepatokines and their functions on systemic metabolism have been interrogated recently as well. The drug development programs targeting hepatokines also have shown inspiring benefits in obesity treatment. In this review, we outline how adipose tissue changes during obesity. Then, we summarize and critically analyze the novel findings on the effects of metabolic "beneficial" and metabolic "harmful" hepatokines to adipose tissue. We also discuss the in-depth molecular mechanism that hepatokines may mediate the liver-adipose tissue crosstalk, the novel technologies targeting hepatokines and their receptors in vivo to explore their functions, and the potential application of these interventions in clinical practice.
Keywords: FGF21; Hepatokine; Liver-adipose tissue crosstalk; Obesity; Therapeutic strategy.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatokines and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Linking Liver Pathophysiology to Metabolism.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 14;9(12):1903. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121903. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34944728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Hepatokines in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.J Transl Int Med. 2019 Dec 31;7(4):143-148. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2019-0029. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Transl Int Med. 2019. PMID: 32010600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatokines and metabolism: Deciphering communication from the liver.Mol Metab. 2021 Feb;44:101138. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101138. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33285302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic PTEN Signaling Regulates Systemic Metabolic Homeostasis through Hepatokines-Mediated Liver-to-Peripheral Organs Crosstalk.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 2;23(7):3959. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073959. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409319 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Adaptation in Obesity and Type II Diabetes: Myokines, Adipokines and Hepatokines.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 22;18(1):8. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010008. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 28025491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Truncated mini LRP1 transports cargo from luminal to basolateral side across the blood brain barrier.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024 Sep 17;21(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12987-024-00573-1. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024. PMID: 39289695 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay between Liver and Adipose Tissue in the Onset of Liver Diseases: Exploring the Role of Vitamin Deficiency.Cells. 2024 Sep 30;13(19):1631. doi: 10.3390/cells13191631. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Polyzos S.A., Kountouras J., Mantzoros C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism. 2019;92:82–97. - PubMed
-
- Kusminski C.M., Bickel P.E., Scherer P.E. Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15(9):639–660. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

