Effects of a long-acting secretin peptide analog alone and in combination with a GLP-1R agonist in a diet-induced obesity mouse model
- PMID: 37390979
- PMCID: PMC10344952
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101765
Effects of a long-acting secretin peptide analog alone and in combination with a GLP-1R agonist in a diet-induced obesity mouse model
Abstract
Objective: Obesity is a major global health problem which can be targeted with new mechanistic diverse pharmacological interventions. Here we evaluate a new long-acting secretin receptor agonist as a potential treatment for obesity.
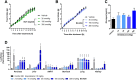
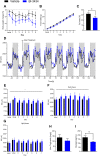
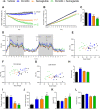
Methods: BI-3434 was designed as a secretin analog with stabilized peptide backbone and attached fatty acid-based half-life extension group. The peptide was evaluated in vitro for its ability to stimulate cAMP accumulation in a cell line stably expressing recombinant secretin receptor. On the functional level, stimulation of lipolysis in primary adipocytes after treatment with BI-3434 was determined. The ability of BI-3434 to activate secretin receptor in vivo was assessed in a cAMP reporter CRE-Luc mouse model. Furthermore, a diet-induced obesity mouse model was used to test the effects of BI-3434 on body weight and food intake following repeated daily subcutaneous administration alone and in combination with a GLP-1R agonist.
Results: BI-3434 potently activated human secretin receptor. However, lipolysis was only weakly induced in primary murine adipocytes. BI-3434 had an extended half-life compared to endogenous secretin and activated target tissues like pancreas, adipose tissue, and stomach in vivo. BI-3434 did not lower food intake in lean or diet-induced obese mice, but it increased energy expenditure after daily administration. This led to a loss of fat mass, which did not translate in a significant effect on body weight. However, treatment in combination with a GLP-1R agonist led to a synergistic effect on body weight loss.
Conclusions: BI-3434 is a highly potent and selective agonist of secretin receptor with an extended pharmacokinetic (PK) profile. Increased energy expenditure after daily treatment with BI-3434 suggests that secretin receptor is involved in metabolic regulation and energy homeostasis. Targeting secretin receptor alone may not be an efficient anti-obesity treatment, but could be combined with anorectic principles like GLP-1R agonists.
Keywords: Combination therapy; Obesity; Peptide treatment; Secretin.
Copyright © 2023 Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH&Co.KG. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Figures


Similar articles
-
BI 456906: Discovery and preclinical pharmacology of a novel GCGR/GLP-1R dual agonist with robust anti-obesity efficacy.Mol Metab. 2022 Dec;66:101633. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101633. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Mol Metab. 2022. PMID: 36356832 Free PMC article.
-
Running on mixed fuel-dual agonistic approach of GLP-1 and GCG receptors leads to beneficial impact on body weight and blood glucose control: A comparative study between mice and non-human primates.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Aug;20(8):1836-1851. doi: 10.1111/dom.13212. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29938884 Free PMC article.
-
Stapled, Long-Acting Xenopus GLP-1-Based Dual GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonists with Potent Therapeutic Efficacy for Metabolic Disease.Mol Pharm. 2021 Aug 2;18(8):2906-2923. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00995. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34240881
-
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on weight loss: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials.BMJ. 2012 Jan 10;344:d7771. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d7771. BMJ. 2012. PMID: 22236411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The value of short- and long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: experience with exenatide.Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(1):61-76. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1103214. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016. PMID: 26439329 Review.
References
-
- WHO Obesity and overweight fact sheet 2020. 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

