Blood purification in sepsis and COVID-19: what´s new in cytokine and endotoxin hemoadsorption
- PMID: 37386575
- PMCID: PMC8978509
- DOI: 10.1186/s44158-022-00043-w
Blood purification in sepsis and COVID-19: what´s new in cytokine and endotoxin hemoadsorption
Abstract
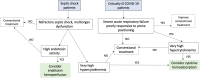
Sepsis and COVID-19 are two clinical conditions that can lead to a dysregulated inflammatory state causing multiorgan dysfunction, hypercytokinemia, and a high risk of death. Specific subgroups of critically ill patients with particular characteristics could benefit from rescue treatment with hemoadsorption. There is a lack of adequately designed randomized controlled trials evaluating the potential benefits of cytokine or endotoxin hemoadsorption. Critically ill COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory failure poorly responsive to conventional treatment could be candidates to receive cytokine hemoadsorption in the presence of high levels of interleukin 6. This treatment can also be suitable for patients with refractory septic shock and hypercytokinemia. In the context of high endotoxin activity, hemoadsorption with polymyxin B could improve clinical parameters and the prognosis of patients with refractory septic shock. Predictive enrichment, using biomarkers or other individual features, identifies potential responders to cytokine, endotoxin, or sequential hemoadsorption. Besides, recognizing the particular subsets of patients likely to respond to one or both types of hemoadsorption will aid the design of future studies that accurately validate the effectiveness of these therapies.
Keywords: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID-19; Cytokine hemoadsorption; Cytosorb; Endotoxin Hemoperfusion; Hypercytokinemia; Polymyxin B; SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia; Sepsis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JCR have received fees from Palex. RF have received fees from Cytosorbents and Estor. The rest of the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytokine Hemoadsorption as Rescue Therapy for Critically Ill Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia With Severe Respiratory Failure and Hypercytokinemia.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 10;8:779038. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.779038. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35083241 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin and Cytokine Sequential Hemoadsorption in Septic Shock and Multi-Organ Failure.Blood Purif. 2022;51(7):630-633. doi: 10.1159/000518229. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Blood Purif. 2022. PMID: 34515070
-
Hemoadsorption by CytoSorb in septic patients: a case series.Crit Care. 2017 Mar 27;21(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1662-9. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28343448 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Utility of Extracorporeal Cytokine Hemoadsorption Therapy: A Literature Review.Blood Purif. 2018;46(4):337-349. doi: 10.1159/000492379. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Blood Purif. 2018. PMID: 30176653 Review.
-
Effect of extracorporeal hemoadsorption in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A narrative review.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 3;14:1074465. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1074465. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817416 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current perspectives in the management of sepsis and septic shock.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 15;11:1431791. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1431791. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39211340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges in Septic Shock: From New Hemodynamics to Blood Purification Therapies.J Pers Med. 2024 Feb 3;14(2):176. doi: 10.3390/jpm14020176. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38392609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous