CDK8 and CDK19: positive regulators of signal-induced transcription and negative regulators of Mediator complex proteins
- PMID: 37378433
- PMCID: PMC10415139
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad538
CDK8 and CDK19: positive regulators of signal-induced transcription and negative regulators of Mediator complex proteins
Abstract
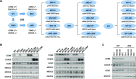
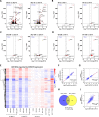
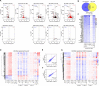
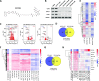
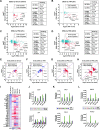
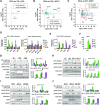
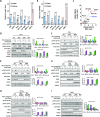
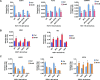
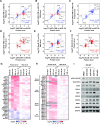
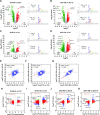
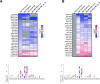
We have conducted a detailed transcriptomic, proteomic and phosphoproteomic analysis of CDK8 and its paralog CDK19, alternative enzymatic components of the kinase module associated with transcriptional Mediator complex and implicated in development and diseases. This analysis was performed using genetic modifications of CDK8 and CDK19, selective CDK8/19 small molecule kinase inhibitors and a potent CDK8/19 PROTAC degrader. CDK8/19 inhibition in cells exposed to serum or to agonists of NFκB or protein kinase C (PKC) reduced the induction of signal-responsive genes, indicating a pleiotropic role of Mediator kinases in signal-induced transcriptional reprogramming. CDK8/19 inhibition under basal conditions initially downregulated a small group of genes, most of which were inducible by serum or PKC stimulation. Prolonged CDK8/19 inhibition or mutagenesis upregulated a larger gene set, along with a post-transcriptional increase in the proteins comprising the core Mediator complex and its kinase module. Regulation of both RNA and protein expression required CDK8/19 kinase activities but both enzymes protected their binding partner cyclin C from proteolytic degradation in a kinase-independent manner. Analysis of isogenic cell populations expressing CDK8, CDK19 or their kinase-inactive mutants revealed that CDK8 and CDK19 have the same qualitative effects on protein phosphorylation and gene expression at the RNA and protein levels, whereas differential effects of CDK8 versus CDK19 knockouts were attributable to quantitative differences in their expression and activity rather than different functions.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Responses to IFN-γ Require Mediator Kinase-Dependent Pause Release and Mechanistically Distinct CDK8 and CDK19 Functions.Mol Cell. 2019 Nov 7;76(3):485-499.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.034. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31495563 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator kinase inhibitors suppress triple-negative breast cancer growth and extend tumor suppression by mTOR and AKT inhibitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 19;121(47):e2414501121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2414501121. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39541354 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of adaptive anoikis resistance promotes metastasis that can be overcome by CDK8/19 Mediator kinase inhibition.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 6:2023.12.04.569970. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.04.569970. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 38106208 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mediator kinase inhibition reverses castration resistance of advanced prostate cancer.J Clin Invest. 2024 Mar 28;134(10):e176709. doi: 10.1172/JCI176709. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38546787 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator kinase inhibition suppresses hyperactive interferon signaling in Down syndrome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 20:2023.07.05.547813. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.05.547813. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2025 Feb 10;13:RP100197. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100197. PMID: 37461585 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Dynamic modes of Notch transcription hubs conferring memory and stochastic activation revealed by live imaging the co-activator Mastermind.Elife. 2024 May 10;12:RP92083. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92083. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38727722 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule inhibitors of transcriptional cyclin-dependent kinases impose HIV-1 latency, presenting "block and lock" treatment strategies.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Mar 6;68(3):e0107223. doi: 10.1128/aac.01072-23. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38319085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lynch C.J., Bernad R., Martinez-Val A., Shahbazi M.N., Nobrega-Pereira S., Calvo I., Blanco-Aparicio C., Tarantino C., Garreta E., Richart-Gines L.et al. .. Global hyperactivation of enhancers stabilizes human and mouse naive pluripotency through inhibition of CDK8/19 Mediator kinases. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020; 22:1223–1238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

