CXCR4-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals for the Imaging and Therapy of Malignant Tumors
- PMID: 37375261
- PMCID: PMC10304366
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28124707
CXCR4-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals for the Imaging and Therapy of Malignant Tumors
Abstract
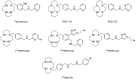
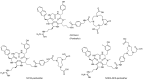
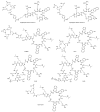
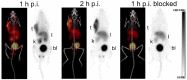
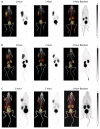
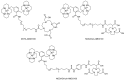
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), also known as fusin or CD184, is a 7-transmembrane helix G-protein-coupled receptor that is encoded by the CXCR4 gene. Involved in various physiological processes, CXCR4 could form an interaction with its endogenous partner, chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12), which is also named SDF-1. In the past several decades, the CXCR4/CXCL12 couple has attracted a large amount of research interest due to its critical functions in the occurrence and development of refractory diseases, such as HIV infection, inflammatory diseases, and metastatic cancer, including breast cancer, gastric cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer. Furthermore, overexpression of CXCR4 in tumor tissues was shown to have a high correlation with tumor aggressiveness and elevated risks of metastasis and recurrence. The pivotal roles of CXCR4 have encouraged an effort around the world to investigate CXCR4-targeted imaging and therapeutics. In this review, we would like to summarize the implementation of CXCR4-targeted radiopharmaceuticals in the field of various kinds of carcinomas. The nomenclature, structure, properties, and functions of chemokines and chemokine receptors are briefly introduced. Radiopharmaceuticals that could target CXCR4 will be described in detail according to their structure, such as pentapeptide-based structures, heptapeptide-based structures, nonapeptide-based structures, etc. To make this review a comprehensive and informative article, we would also like to provide the predictive prospects for the CXCR4-targeted species in future clinical development.
Keywords: CXCL12; CXCR4; chemokine receptor; metastatic cancer; radiopharmaceuticals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
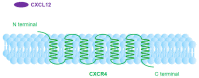
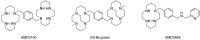

Similar articles
-
Fluorescent CXCL12AF647 as a novel probe for nonradioactive CXCL12/CXCR4 cellular interaction studies.Cytometry A. 2004 Oct;61(2):178-88. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20070. Cytometry A. 2004. PMID: 15382150
-
The CXCR4/SDF-1 chemokine receptor axis: a new target therapeutic for non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2008 Dec;3(12):1379-83. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31818dda9d. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19057260 Review.
-
Biological/pathological functions of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axes in the pathogenesis of bladder cancer.Int J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;22(6):991-1000. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1187-x. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29022185 Review.
-
CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 1;16(11):2927-31. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2329. Epub 2010 May 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20484021 Review.
-
Effect of CXCL12 and Its Receptors on Unpredictable Renal Cell Carcinoma.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2020 Aug;18(4):e337-e342. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.11.004. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31882334 Review.
Cited by
-
PET imaging of CXCR4 expression using [18F]AlF-NOTA-QHY-04 for hematologic malignancy and solid tumors.Theranostics. 2024 Sep 30;14(16):6337-6349. doi: 10.7150/thno.99025. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39431004 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine receptor PET imaging: Bridging molecular insights with clinical applications.Nucl Med Biol. 2024 Jul-Aug;134-135:108912. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2024.108912. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Nucl Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38691942 Review.
References
-
- Fakhari A., Aghanejad A., Jalilian A.R., Gharepapagh E. Recent developments in targeted imaging of CXCR4-chemokine receptor. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018;317:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s10967-018-5910-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

