Drug Target Identification and Drug Repurposing in Psoriasis through Systems Biology Approach, DNN-Based DTI Model and Genome-Wide Microarray Data
- PMID: 37373186
- PMCID: PMC10298553
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241210033
Drug Target Identification and Drug Repurposing in Psoriasis through Systems Biology Approach, DNN-Based DTI Model and Genome-Wide Microarray Data
Abstract
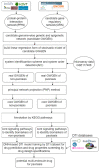
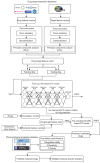
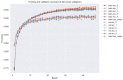
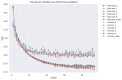
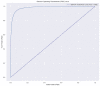
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease that affects millions of people worldwide. In 2014, psoriasis was recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a serious non-communicable disease. In this study, a systems biology approach was used to investigate the underlying pathogenic mechanism of psoriasis and identify the potential drug targets for therapeutic treatment. The study involved the construction of a candidate genome-wide genetic and epigenetic network (GWGEN) through big data mining, followed by the identification of real GWGENs of psoriatic and non-psoriatic using system identification and system order detection methods. Core GWGENs were extracted from real GWGENs using the Principal Network Projection (PNP) method, and the corresponding core signaling pathways were annotated using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways. Comparing core signaling pathways of psoriasis and non-psoriasis and their downstream cellular dysfunctions, STAT3, CEBPB, NF-κB, and FOXO1 are identified as significant biomarkers of pathogenic mechanism and considered as drug targets for the therapeutic treatment of psoriasis. Then, a deep neural network (DNN)-based drug-target interaction (DTI) model was trained by the DTI dataset to predict candidate molecular drugs. By considering adequate regulatory ability, toxicity, and sensitivity as drug design specifications, Naringin, Butein, and Betulinic acid were selected from the candidate molecular drugs and combined into potential multi-molecule drugs for the treatment of psoriasis.
Keywords: DNN-based DTI model; DTI databases; bid data mining; core signaling pathways; drug design specifications; multi-molecule drug; pathogenic mechanism of psoriasis; systems biology method.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systems Biology Methods via Genome-Wide RNA Sequences to Investigate Pathogenic Mechanisms for Identifying Biomarkers and Constructing a DNN-Based Drug-Target Interaction Model to Predict Potential Molecular Drugs for Treating Atopic Dermatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 4;25(19):10691. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910691. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409019 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Drug Targets of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma through a Systems Biology Method and Genome-Wide Microarray Data for Drug Discovery by Deep Learning and Drug Design Specifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10409. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810409. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142321 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Drug Design for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer and Advanced Bladder Cancer by Genome-Wide Microarray Data and Deep Learning Method with Drug Design Specifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13869. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213869. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430344 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative clinical transcriptomics analyses for new therapeutic intervention strategies: a psoriasis case study.Drug Discov Today. 2014 Sep;19(9):1364-71. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2014.03.015. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Drug Discov Today. 2014. PMID: 24662034 Review.
-
The current landscape of psoriasis genetics in 2020.J Dermatol Sci. 2020 Jul;99(1):2-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.05.008. Epub 2020 May 28. J Dermatol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32536600 Review.
Cited by
-
Systems Biology Methods via Genome-Wide RNA Sequences to Investigate Pathogenic Mechanisms for Identifying Biomarkers and Constructing a DNN-Based Drug-Target Interaction Model to Predict Potential Molecular Drugs for Treating Atopic Dermatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 4;25(19):10691. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910691. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409019 Free PMC article.
-
Principles, applications, and future of artificial intelligence in dermatology.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 12;10:1278232. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1278232. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37901399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMMVF-DTI: A Novel Model Predicting Drug-Target Interactions Based on Attention Mechanism and Multi-View Fusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 15;24(18):14142. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814142. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization Global Report on Psoriasis. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

