p53 Affects Zeb1 Interactome of Breast Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 37372954
- PMCID: PMC10297930
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24129806
p53 Affects Zeb1 Interactome of Breast Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
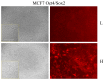
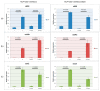
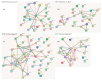
P53 is a critical tumor suppressor that protects the integrity of genome and prevents cells from malignant transformation, including metastases. One of the driving forces behind the onset of metastases is the epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) program. Zeb1 is one of the key transcription factors that govern EMT (TF-EMT). Therefore, the interaction and mutual influence of p53 and Zeb1 plays a critical role in carcinogenesis. Another important feature of tumors is their heterogeneity mediated by the presence of so-called cancer stem cells (CSCs). To this end, we have developed a novel fluorescent reporter-based approach to enrich the population of CSCs in MCF7 cells with inducible expression of Zeb1. Using these engineered cell lines, we studied the effect of p53 on Zeb1 interactomes isolated from both CSCs and regular cancer cells. By employing co-immunoprecipitations followed by mass spectrometry, we found that the composition of Zeb1 interactome was affected not only by the p53 status but also by the level of Oct4/Sox2 expression, indicating that stemness likely affects the specificity of Zeb1 interactions. This study, together with other proteomic studies of TF-EMT interactomes, provides a framework for future molecular analyses of biological functions of Zeb1 at all stages of oncogenesis.
Keywords: Zeb1; breast cancer; cancer stem cells; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT); metastasis; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Downregulation of DAPK1 promotes the stemness of cancer stem cells and EMT process by activating ZEB1 in colorectal cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Jan;97(1):89-102. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1716-8. Epub 2018 Nov 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30460377
-
Proteomic Analysis of Zeb1 Interactome in Breast Carcinoma Cells.Molecules. 2021 May 24;26(11):3143. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113143. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34074001 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Hierarchy and Cooperation of EMT Master Transcription Factors in Breast Cancer Metastasis.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 May;19(5):784-798. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0532. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33500360 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic functions of the EMT-related transcription factor ZEB1 in breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2020 Feb 3;18(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02240-z. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32014049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZEB1: Catalyst of immune escape during tumor metastasis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Sep;153:113490. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113490. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36076506 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics and Its Applications in Cancers 2.0.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 18;25(8):4447. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084447. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pozdnyakov D.Y., Shuvalov O.Y., Barlev N.A., Mittenberg A.G. Role of Zeb1 EMT-TF in metastasis and carcinogenesis. Tsitologiia. 2019;61:915–925. doi: 10.1134/S0041377119110087. (In Russian) - DOI
-
- Pozdnyakov D.Y., Shuvalov O.Y., Barlev N.A., Mittenberg A.G. Post-transcriptional regulation of Zeb1 EMT-TF activity in human breast carcinomae. Tsitologiia. 2020;62:3–15. doi: 10.31857/S0041377120010071. (In Russian) - DOI
-
- Tevaarwerk A.J., Gray R.J., Schneider B.P., Smith M.L., Wagner L.I., Fetting J.H., Davidson N., Goldstein L.J., Miller K.D., Sparano J.A. Survival in patients with metastatic recurrent breast cancer after adjuvant chemotherapy: Little evidence of improvement over the past 30 years. Cancer. 2013;119:1140–1148. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27819. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

