Rabconnectin-3α/DMXL2 Is Locally Enriched at the Synaptic Ribbon of Rod Photoreceptor Synapses
- PMID: 37371135
- PMCID: PMC10297199
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12121665
Rabconnectin-3α/DMXL2 Is Locally Enriched at the Synaptic Ribbon of Rod Photoreceptor Synapses
Abstract
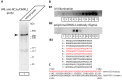
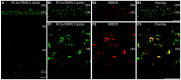
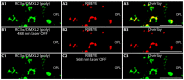
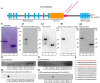
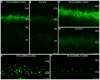
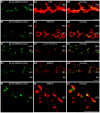
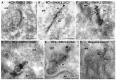
Ribbon synapses reliably transmit synaptic signals over a broad signalling range. Rod photoreceptor ribbon synapses are capable of transmitting signals generated by the absorption of single photons. The high precision of ribbon synapses emphasizes the need for particularly efficient signalling mechanisms. Synaptic ribbons are presynaptic specializations of ribbon synapses and are anchored to the active zone. Synaptic ribbons bind many synaptic vesicles that are delivered to the active zone for continuous and faithful signalling. In the present study we demonstrate with independent antibodies at the light- and electron microscopic level that rabconnectin-3α (RC3α)-alternative name Dmx-like 2 (DMXL2)-is localized to the synaptic ribbons of rod photoreceptor synapses in the mouse retina. In the brain, RC3α-containing complexes are known to interact with important components of synaptic vesicles, including Rab3-activating/inactivating enzymes, priming proteins and the vesicular H+-ATPase that acidifies the synaptic vesicle lumen to promote full neurotransmitter loading. The association of RC3α/DMXL2 with rod synaptic ribbons of the mouse retina could enable these structures to deliver only fully signalling-competent synaptic vesicles to the active zone thus contributing to reliable synaptic communication.
Keywords: DMXL2; Rab3; rabconnectin-3α; retina; ribbon synapse; vesicular H+-ATPase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early Changes in Exo- and Endocytosis in the EAE Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis Correlate with Decreased Synaptic Ribbon Size and Reduced Ribbon-Associated Vesicle Pools in Rod Photoreceptor Synapses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 6;22(19):10789. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910789. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639129 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of synaptic vesicle proteins in the mammalian retina identifies obligatory and facultative components of ribbon synapses.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Apr;11(4):1335-48. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00542.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10103129
-
Synaptic ribbons foster active zone stability and illumination-dependent active zone enrichment of RIM2 and Cav1.4 in photoreceptor synapses.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 6;10(1):5957. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62734-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32249787 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission at rod and cone ribbon synapses in the retina.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Sep;473(9):1469-1491. doi: 10.1007/s00424-021-02548-9. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 33779813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynamic architecture of photoreceptor ribbon synapses: cytoskeletal, extracellular matrix, and intramembrane proteins.Vis Neurosci. 2011 Nov;28(6):453-71. doi: 10.1017/S0952523811000356. Vis Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22192503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Presynaptic Proteins and Their Roles in Visual Processing by the Retina.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2024 Sep;10(1):347-375. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-101322-111204. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38621251 Review.
-
Retinal Cell Biology in Health and Disease.Cells. 2024 Feb 6;13(4):297. doi: 10.3390/cells13040297. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38391910 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

