Astrocyte and Neuronal Panx1 Support Long-Term Reference Memory in Mice
- PMID: 37365910
- PMCID: PMC10326369
- DOI: 10.1177/17590914231184712
Astrocyte and Neuronal Panx1 Support Long-Term Reference Memory in Mice
Abstract
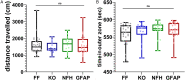
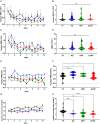
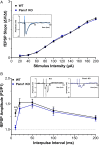
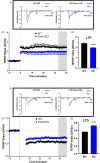
Pannexin 1 (Panx1) is an ubiquitously expressed protein that forms plasma membrane channels permeable to anions and moderate-sized signaling molecules (e.g., ATP, glutamate). In the nervous system, activation of Panx1 channels has been extensively shown to contribute to distinct neurological disorders (epilepsy, chronic pain, migraine, neuroAIDS, etc.), but knowledge of the extent to which these channels have a physiological role remains restricted to three studies supporting their involvement in hippocampus dependent learning. Given that Panx1 channels may provide an important mechanism for activity-dependent neuron-glia interaction, we used Panx1 transgenic mice with global and cell-type specific deletions of Panx1 to interrogate their participation in working and reference memory. Using the eight-arm radial maze, we show that long-term spatial reference memory, but not spatial working memory, is deficient in Panx1-null mice and that both astrocyte and neuronal Panx1 contribute to the consolidation of long-term spatial memory. Field potential recordings in hippocampal slices of Panx1-null mice revealed an attenuation of both long-term potentiation (LTP) of synaptic strength and long-term depression (LTD) at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses without alterations of basal synaptic transmission or pre-synaptic paired-pulse facilitation. Our results implicate both neuronal and astrocyte Panx1 channels as critical players for the development and maintenance of long-term spatial reference memory in mice.
Keywords: long-term potentiation; pannexin; radial maze; spatial memory; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
Price Obot is currently affiliated to Department of Emergency Medicine, Penn State Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA, USA.
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Update of
-
Astrocyte and neuronal Panx1 support long-term reference memory in mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 18:2023.01.16.524236. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.16.524236. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ASN Neuro. 2023 Jan-Dec;15:17590914231184712. doi: 10.1177/17590914231184712 PMID: 36711845 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Astrocyte and neuronal Panx1 support long-term reference memory in mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 18:2023.01.16.524236. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.16.524236. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ASN Neuro. 2023 Jan-Dec;15:17590914231184712. doi: 10.1177/17590914231184712 PMID: 36711845 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Pannexin1 stabilizes synaptic plasticity and is needed for learning.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051767. Epub 2012 Dec 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23284764 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin-1 Modulates Inhibitory Transmission and Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity.Biomolecules. 2023 May 25;13(6):887. doi: 10.3390/biom13060887. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371467 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin-4 water channels and synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus.Neurochem Int. 2013 Dec;63(7):702-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 15. Neurochem Int. 2013. PMID: 23684954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the structure and activation mechanisms of metabolite-releasing Pannexin 1 channels.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Aug 31;51(4):1687-1699. doi: 10.1042/BST20230038. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37622532 Review.
Cited by
-
NMDAR-mediated activation of pannexin1 channels contributes to the detonator properties of hippocampal mossy fiber synapses.iScience. 2024 Apr 6;27(5):109681. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109681. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38680664 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin1 Mediates Early-Life Seizure-Induced Social Behavior Deficits.ASN Neuro. 2024;16(1):2371164. doi: 10.1080/17590914.2024.2371164. Epub 2024 Jul 16. ASN Neuro. 2024. PMID: 39024558 Free PMC article.
-
Efferocytosis by macrophages in physiological and pathological conditions: regulatory pathways and molecular mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2024 May 8;15:1275203. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1275203. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38779685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanistic effects of acupuncture in rodent neurodegenerative disease models: a literature review.Front Neurosci. 2024 Mar 4;18:1323555. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1323555. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38500484 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anselmi F., Hernandez V. H., Crispino G., Seydel A., Ortolano S., Roper S. D., Kessaris N., Richardson W., Rickheit G., Filippov M. A., Monyer H., Mammano F. (2008). ATP Release through connexin hemichannels and gap junction transfer of second messengers propagate Ca2 + signals across the inner ear. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 18770–18775. 10.1073/pnas.0800793105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ardiles A. O., Flores-Munoz C., Toro-Ayala G., Cardenas A. M., Palacios A. G., Munoz P., Fuenzalida M., Saez J. C., Martinez A. D. (2014). Pannexin 1 regulates bidirectional hippocampal synaptic plasticity in adult mice. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 8, 326. 10.3389/fncel.2014.00326 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
