Inhibition of autophagy; an opportunity for the treatment of cancer resistance
- PMID: 37363731
- PMCID: PMC10290173
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1177440
Inhibition of autophagy; an opportunity for the treatment of cancer resistance
Abstract
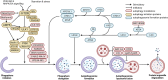
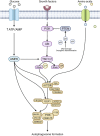
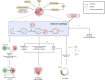
The process of macroautophagy plays a pivotal role in the degradation of long-lived, superfluous, and damaged proteins and organelles, which are later recycled for cellular use. Normal cells rely on autophagy to combat various stressors and insults to ensure survival. However, autophagy is often upregulated in cancer cells, promoting a more aggressive phenotype that allows mutated cells to evade death after exposure to therapeutic treatments. As a result, autophagy has emerged as a significant factor in therapeutic resistance across many cancer types, with underlying mechanisms such as DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and immune evasion. This review provides a comprehensive summary of the role of autophagy in therapeutic resistance and the limitations of available autophagic inhibitors in cancer treatment. It also highlights the urgent need to explore new inhibitors that can synergize with existing therapies to achieve better patient treatment outcomes. Advancing research in this field is crucial for developing more effective treatments that can help improve the lives of cancer patients.
Keywords: autophagy; autophagy mechanisms; cancer; drug resisitance; therapeutic resistance.
Copyright © 2023 Tonkin-Reeves, Giuliani and Price.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Autophagy for Cancer Treatment and Tumor Chemosensitization.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 19;11(10):1599. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101599. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31635099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of selective autophagy in Drosophila.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2020;354:63-105. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2019.08.003. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32475477 Review.
-
The role of autophagy in HER2-targeted therapy.Swiss Med Wkly. 2019 Oct 27;149:w20138. doi: 10.4414/smw.2019.20138. eCollection 2019 Oct 7. Swiss Med Wkly. 2019. PMID: 31656036 Review.
-
Autophagy Takes Center Stage as a Possible Cancer Hallmark.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 22;10:586069. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.586069. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To die or not to die: that is the autophagic question.Curr Mol Med. 2008 Mar;8(2):78-91. doi: 10.2174/156652408783769616. Curr Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18336289 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of NNMT enhances drug sensitivity in lung cancer cells through mediation of autophagy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 5;15:1415310. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1415310. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39035994 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting autophagy can synergize the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors against therapeutic resistance: New promising strategy to reinvigorate cancer therapy.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 3;10(18):e37376. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37376. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39309904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

