Insights into fourth generation selective inhibitors of (C797S) EGFR mutation combating non-small cell lung cancer resistance: a critical review
- PMID: 37350862
- PMCID: PMC10282734
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra02347h
Insights into fourth generation selective inhibitors of (C797S) EGFR mutation combating non-small cell lung cancer resistance: a critical review
Abstract
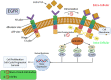
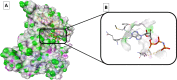
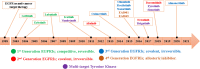
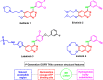
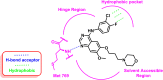
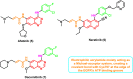
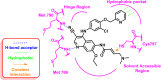
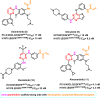
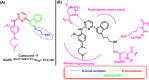
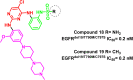
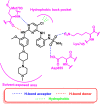
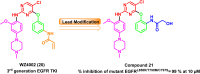
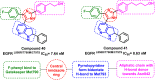
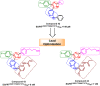
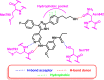
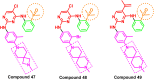
Lung cancer is the second most common cause of morbidity and mortality among cancer types worldwide, with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) representing the majority of most cases. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR TKIs) are among the most commonly used targeted therapy to treat NSCLC. Recent years have seen the evaluation of many synthetic EGFR TKIs, most of which showed therapeutic activity in pertinent models and were classified as first, second, and third-generation. The latest studies have concluded that their efficacy was also compromised by additional acquired mutations, including C797S. Because second- and third-generation EGFR TKIs are irreversible inhibitors, they are ineffective against C797S containing EGFR triple mutations (Del19/T790M/C797S and L858R/T790M/C797S). Therefore, there is an urgent unmet medical need to develop next-generation EGFR TKIs that selectively inhibit EGFR triple mutations via a non-irreversible mechanism. This review covers the fourth-generation EGFR-TKIs' most recent design with their essential binding interactions, the clinical difficulties, and the potential outcomes of treating patients with EGFR mutation C797S resistant to third-generation EGFR-TKIs was also discussed. Moreover, the utilization of various therapeutic strategies, including multi-targeting drugs and combination therapies, has also been reviewed.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that they have no known financial or interpersonal conflicts that would have appeared to impact the research presented in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chronicles of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Targeting EGFR C797S Containing Triple Mutations.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022 Jan 1;30(1):19-27. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2021.047. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022. PMID: 34074804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors to overcome C797S mutation in non-small cell lung cancer (2019-2024).RSC Med Chem. 2024 Aug 30;15(10):3371-94. doi: 10.1039/d4md00384e. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39246743 Review.
-
Response to Brigatinib Targeted Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 19 Deletion, T790M, and cis-C797S Triple Mutations: A Case Report.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 29;24(1):602. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010602. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614045 Free PMC article.
-
Audit of Molecular Mechanisms of Primary and Secondary Resistance to Various Generations of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Known Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in a Tertiary Centre.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022 Nov;34(11):e451-e462. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022. PMID: 35810049
-
Design, synthesis and evaluation of the Brigatinib analogues as potent inhibitors against tertiary EGFR mutants (EGFRdel19/T790M/C797S and EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S).Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Sep 15;72:128729. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128729. Epub 2022 Apr 9. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35413415
Cited by
-
Lactate-Induced HBEGF Shedding and EGFR Activation: Paving the Way to a New Anticancer Therapeutic Opportunity.Cells. 2024 Sep 13;13(18):1533. doi: 10.3390/cells13181533. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329717 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing molecular hybridization approach to discover novel quinoline EGFR-TK inhibitors for cancer treatment.Future Med Chem. 2024;16(11):1087-1107. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2342201. Epub 2024 May 9. Future Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38722235
-
Targeted Inhibitors of EGFR: Structure, Biology, Biomarkers, and Clinical Applications.Cells. 2023 Dec 25;13(1):47. doi: 10.3390/cells13010047. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38201251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics-driven discovery of novel EGFR kinase inhibitors as anti-cancer therapeutics: In silico screening and in vitro evaluation.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 16;19(4):e0298326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298326. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38625872 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrrolizine/indolizine-bearing (un)substituted isoindole moiety: design, synthesis, antiproliferative and MDR reversal activities, and in silico studies.RSC Adv. 2023 Oct 20;13(44):30753-30770. doi: 10.1039/d3ra05310e. eCollection 2023 Oct 18. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37869384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warnakulasuriya S. Kujan O. Aguirre-Urizar J. M. Bagan J. V. González-Moles M. Á. Kerr A. R. Lodi G. Mello F. W. Monteiro L. Ogden G. R. Oral Dis. 2021;27:1862–1880. - PubMed
-
- Sain R. K. Chouhan R. Bagri L. P. Bajpa A. J. Cancer Res. Updates. 2012;1:129–152.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

