The human embryo selection arena is associated with transposable element activity
- PMID: 37348048
- PMCID: PMC10281567
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002153
The human embryo selection arena is associated with transposable element activity
Abstract
Our current understanding of early human development is limited. A study in PLOS Biology found a previously undefined group of cells that diverges from the main lineages and undergo apoptosis through the activity of young transposable elements.
Copyright: © 2023 Osnato et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
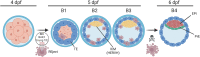
Comment on
-
A new human embryonic cell type associated with activity of young transposable elements allows definition of the inner cell mass.PLoS Biol. 2023 Jun 20;21(6):e3002162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002162. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37339119 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
A new human embryonic cell type associated with activity of young transposable elements allows definition of the inner cell mass.PLoS Biol. 2023 Jun 20;21(6):e3002162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002162. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37339119 Free PMC article.
-
Deconstructing genomic plasticity in the early human embryo: transposable elements having their way!J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Sep;41(9):2225-2226. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03247-x. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024. PMID: 39225841 No abstract available.
-
Effects of assisted reproductive technologies on transposon regulation in the mouse pre-implanted embryo.Hum Reprod. 2019 Apr 1;34(4):612-622. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez020. Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 30865273
-
Perspective: transposable elements, parasitic DNA, and genome evolution.Evolution. 2001 Jan;55(1):1-24. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2001.tb01268.x. Evolution. 2001. PMID: 11263730 Review.
-
DNA methylation dynamics at transposable elements in mammals.Essays Biochem. 2019 Dec 20;63(6):677-689. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190039. Essays Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31654072 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

