PI3K/PTEN/mTOR pathway dynamic tracking and prognostic value in HR+/HER2- BC patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a cohort study
- PMID: 37344170
- PMCID: PMC11503171
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp-2023-208856
PI3K/PTEN/mTOR pathway dynamic tracking and prognostic value in HR+/HER2- BC patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a cohort study
Abstract
Aims: Hormone receptor-positive (HR)+/HER2- breast cancer (BC) is highly heterogeneous, with PI3K/PTEN/mTOR pathway alterations emerging as possible players within this complexity. We longitudinally tracked PI3K/PTEN/mTOR pathway dynamics from baseline biopsy to residual disease (RD)-and to metastases in case of relapse-in HR+/HER2- BC patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT).
Methods: HR+/HER2- BC patients with RD after NACT were identified. We assessed PIK3CA mutational, Pten-loss and phosphorylation levels of mTOR and its substrates (p70S6K and 4EBP1) on baseline biopsies and matched RD samples; in case of disease relapse, we also assessed PIK3CA mutational status on metastatic samples. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was adopted as endpoint.
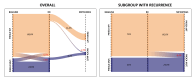
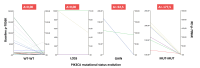
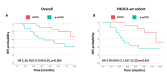
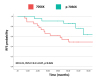
Results: 92 patient were included. The conversion rate of PIK3CA mutational status was 12.8%; 1 patient acquired PIK3CA mutation at relapse; the rate of Pten conversion was 33.3%; mTOR phosphorylation levels significantly increased from baseline biopsy to RD, while its substrates significantly decreased. Baseline phosphorylated-mTOR significantly predicted poorer RFS in patients with PIK3CA wild-type status; baseline phosphorylated-70S6K was positively associated with RFS.
Conclusions: We observed that PI3K/PTEN/mTOR pathway is highly dynamic under NACT exposure and the assessment of PIK3CA mutations may capture only a small fraction of such complexity. In this context, mTOR activation trough alternative pathways with respect to PIK3CA signalling may have a crucial role in shaping the molecular landscape of HR+/HER2- BC with RD after NACT. It is imperative to further elucidate the role of PIK3CA and mTOR-dependent pathways in shaping chemoresistance and endocrine resistance in high-risk HR+/HER2- early/locally advanced BC patients.
Keywords: BREAST CANCER; IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY; NEOPLASMS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: FM received personal fee from Roche, Novartis and Gilead, outside the submitted manuscript. GG reports personal fee from Novartis, Eli Lilly, and Gilead outside the submitted work. VG reports personal fees for advisory board membership from Eisai, Eli Lilly, Exact Sciences, Gilead, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, Olema Oncology and Sanofi; personal fees as an invited speaker from Amgen, Eli Lilly, GSK, Astra Zeneca, Novartis; personal fees for expert testimony from Eli Lilly; institutional funding as a local PI from AstraZeneca, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, MSD, Nerviano, Novartis, Roche and Synton Biopharmaceutical. MF has been involved in consulting/advisory roles in Astellas Pharma, Tesaro, MSD, Pierre Fabre, Astra Zeneca, Incyte, GlaxoSmithKline, Diaceutics and Roche, received research funding from Astellas Pharma, QED Therapeutics, and Macrophage Pharma and is supported by grants from the Italian Health Ministry/Veneto region research program NET-2016-02363853 and AIRC 5 per mille 2019 (ID. 22759 programme). MVD reports personal fees from Eli Lilly, MSD, Exact Sciences, Novartis, Pfizer, Seagen, outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PIK3CA mutations, phosphatase and tensin homolog, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and adjuvant tamoxifen resistance in postmenopausal breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Jan 27;16(1):R13. doi: 10.1186/bcr3606. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24467828 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Frequent mutational activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Dec 15;18(24):6784-91. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1785. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23092874 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite Prognostic Impact of Single PTEN-loss and PIK3CA Mutations in Early High-risk Breast Cancer.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2019 May-Jun;16(3):195-206. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20125. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31018950 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: the important role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR in estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2018 Jul;25(4):392-401. doi: 10.1007/s12282-017-0812-x. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29086897 Review.
-
Targeting PIK3CA Alterations in Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: New Therapeutic Approaches and Practical Considerations.Clin Breast Cancer. 2020 Aug;20(4):e439-e449. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32278641 Review.
Cited by
-
Select gene mutations associated with survival outcomes in ER-positive ERBB2-negative early-stage invasive breast cancer: A single-institutional tissue bank study.Cancer Med. 2024 Jul;13(14):e70035. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70035. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39031010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Breast cancer. 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer#:~:text=I... Available.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
