Diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction using a combination of circulating circular RNA cZNF292 and clinical information based on machine learning
- PMID: 37323876
- PMCID: PMC10264944
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.299
Diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction using a combination of circulating circular RNA cZNF292 and clinical information based on machine learning
Abstract
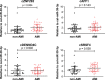
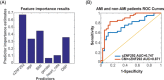
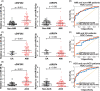
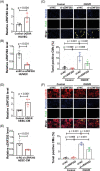
Circulating circular RNAs (circRNAs) are emerging as novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Machine learning can provide optimal predictions on the diagnosis of diseases. Here we performed a proof-of-concept study to determine if combining circRNAs with an artificial intelligence approach works in diagnosing CVD. We used acute myocardial infarction (AMI) as a model setup to prove the claim. We determined the expression level of five hypoxia-induced circRNAs, including cZNF292, cAFF1, cDENND4C, cTHSD1, and cSRSF4, in the whole blood of coronary angiography positive AMI and negative non-AMI patients. Based on feature selection by using lasso with 10-fold cross validation, prediction model by logistic regression, and ROC curve analysis, we found that cZNF292 combined with clinical information (CM), including age, gender, body mass index, heart rate, and diastolic blood pressure, can predict AMI effectively. In a validation cohort, CM + cZNF292 can separate AMI and non-AMI patients, unstable angina and AMI patients, acute coronary syndromes (ACS), and non-ACS patients. RNA stability study demonstrated that cZNF292 was stable. Knockdown of cZNF292 in endothelial cells or cardiomyocytes showed anti-apoptosis effects in oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation. Thus, we identify circulating cZNF292 as a potential biomarker for AMI and construct a prediction model "CM + cZNF292."
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; biomarker; cZNF292; circular RNA; machine learning.
© 2023 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and Characterization of Hypoxia-Regulated Endothelial Circular RNA.Circ Res. 2015 Oct 23;117(10):884-90. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306319. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 26377962
-
Hypoxia-induced circRNAs encoded by PPARA are highly expressed in human cardiomyocytes and are potential clinical biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Mar 12;29(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01753-3. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38475969 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal CircRNAs in Circulation Serve as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Acute Myocardial Infarction.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Apr 11;29(4):149. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2904149. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38682191
-
Collaborative CRISPR-Cas System-Enabled Detection of Circulating Circular RNA for Reliable Monitoring of Acute Myocardial Infarction.Small. 2024 Nov;20(45):e2402895. doi: 10.1002/smll.202402895. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Small. 2024. PMID: 39023080
-
API expert consensus document on management of ischemic heart disease.J Assoc Physicians India. 2006 Jun;54:469-80. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006. PMID: 16909697 Review.
Cited by
-
From multi-omics approaches to personalized medicine in myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Oct 30;10:1250340. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1250340. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37965091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Multifaceted Biologically Relevant Roles of circRNAs: From Regulation, Translation to Biomarkers.Cells. 2023 Dec 10;12(24):2813. doi: 10.3390/cells12242813. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research trends and hotspots of circular RNA in cardiovascular disease: A bibliometric analysis.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Apr 16;9(3):930-944. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.04.002. eCollection 2024 Sep. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 38680417 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in breast cancer diagnosis, treatment and prognosis.Oncol Res. 2023 Dec 28;32(2):241-249. doi: 10.32604/or.2023.046582. eCollection 2023. Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 38186573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jusic A, Devaux Y, EU‐CardioRNA COST Action (CA17129) . Mitochondrial noncoding RNA‐regulatory network in cardiovascular disease. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020;115(3):23. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez A, de Boer RA, Richards AM, et al. Cardiac remodelling—Part 1: From cells and tissues to circulating biomarkers. A review from the study group on biomarkers of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2022;24(6):927‐943. - PubMed
-
- Wang GK, Zhu JQ, Zhang JT, et al. Circulating microRNA: a novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(6):659‐666. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
