Open decortication for patients presenting with stage III tuberculous empyema with low density lines on CT imaging
- PMID: 37316645
- PMCID: PMC10267101
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36420-w
Open decortication for patients presenting with stage III tuberculous empyema with low density lines on CT imaging
Abstract
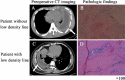
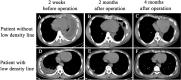
To explore the influence of CT findings on the optimal timing of open decorticationin patients with stage III tuberculous empyema. A total of 80 patients with stage III tuberculous empyema who had undergone open decortications were recruited; 44 patients had chest CT findings indicating low-density lines, while 36 patients did not show this imaging finding. Demographic data, perioperative data and preoperative and postoperative chest CT images were collected. In the low-density line group, the duration of disease (P = 0.0030) and the preoperative anti-tuberculosis time (P = 0.0016) were longer than those of the group without low-density lines, and the ESR (P = 0.0218), CRP (P = 0.0027) and leukocyte count (P = 0.0339) were lower in the low-density line group. Additionally, in the median operative time (P = 0.0003), intraoperative blood loss (P < 0.0001), volume of catheter drainage during 48 h after operation (P = 0.0067), chest tube duration (P < 0.0001), and length of hospital stay (P = 0.0154) were significantly lower in the low-density line group than in the group without low-density lines. A total of 88.64% of participants in the low-density line group showed hyperplasia with hyaline degeneration in pathological examination, which was observed only in 41.67% of patients without low-density lines. In addition, gaseous necrosis was considerably higher in patients without a low-density line (P = 0.004), while the low-density line group had a higher rate of treatment success (P < 0.05). Patients with stage III tuberculous empyema presenting with low-density lines around the thickened fibrous pleural rind on preoperative CT imaging may be good candidates for open decortication.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Uniportal Thoracoscopic Decortication for Stage III Tuberculous Empyema With Severe Rib Crowding.Ann Thorac Surg. 2021 Jul;112(1):289-294. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2020.07.067. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Ann Thorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 33065049
-
Thoracoscopic Decortication of Stage III Tuberculous Empyema Is Effective and Safe in Selected Cases.Ann Thorac Surg. 2017 Nov;104(5):1688-1694. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2017.06.038. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017. PMID: 28964422
-
Application of Thoracoscopic Hybrid Surgery in the Treatment of Stage III Tuberculous Empyema.Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;21(6):523-8. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.15-00158. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 26278117 Free PMC article.
-
[Decortication in Pleural Empyema: Reasonable Effects on Lung Function?].Zentralbl Chir. 2016 Sep;141 Suppl 1:S18-25. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-112025. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Zentralbl Chir. 2016. PMID: 27607885 Review. German.
-
Tuberculous empyema.Semin Respir Infect. 1999 Mar;14(1):82-7. Semin Respir Infect. 1999. PMID: 10197400 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors involved in the conversion from video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery decortication to open thoracotomy in non-complicated, non-MDR/XDR stage III tuberculous empyema patients: A retrospective intention-to-treat study.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 8;10(16):e35939. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35939. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39224388 Free PMC article.
-
The safety and efficacy of decortication for stage III drug-resistant tuberculous empyema.Interdiscip Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2023 Nov 2;37(5):ivad166. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivad166. Interdiscip Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2023. PMID: 37812210 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

