EFdA efficiently suppresses HIV replication in the male genital tract and prevents penile HIV acquisition
- PMID: 37306625
- PMCID: PMC10470584
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.02224-22
EFdA efficiently suppresses HIV replication in the male genital tract and prevents penile HIV acquisition
Abstract
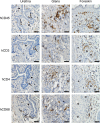
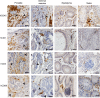
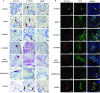
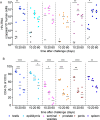
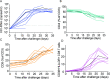
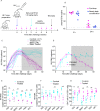
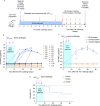
Sexually transmitted HIV infections in heterosexual men are acquired through the penis. Low adherence to condom usage and the fact that 40% of circumcised men are not protected indicate the need for additional prevention strategies. Here, we describe a new approach to evaluate the prevention of penile HIV transmission. We demonstrated that the entire male genital tract (MGT) of bone marrow/liver/thymus (BLT) humanized mice is repopulated with human T and myeloid cells. The majority of the human T cells in the MGT express CD4 and CCR5. Direct penile exposure to HIV leads to systemic infection including all tissues of the MGT. HIV replication throughout the MGT was reduced 100-1,000-fold by treatment with 4'-ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine (EFdA), resulting in the restoration of CD4+ T cell levels. Importantly, systemic preexposure prophylaxis with EFdA effectively protects from penile HIV acquisition. IMPORTANCE Over 84.2 million people have been infected by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) during the past 40 years, most through sexual transmission. Men comprise approximately half of the HIV-infected population worldwide. Sexually transmitted HIV infections in exclusively heterosexual men are acquired through the penis. However, direct evaluation of HIV infection throughout the human male genital tract (MGT) is not possible. Here, we developed a new in vivo model that permits, for the first time, the detail analysis of HIV infection. Using BLT humanized mice, we showed that productive HIV infection occurs throughout the entire MGT and induces a dramatic reduction in human CD4 T cells compromising immune responses in this organ. Antiretroviral treatment with novel drug EFdA suppresses HIV replication in all tissues of the MGT, restores normal levels of CD4 T cells and is highly efficient at preventing penile transmission.
Keywords: EFdA; HIV pathogenesis; HIV prevention; HIV treatment; human immunodeficiency virus; male genital tract; penile infection; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficient Inhibition of HIV Replication in the Gastrointestinal and Female Reproductive Tracts of Humanized BLT Mice by EFdA.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 20;11(7):e0159517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159517. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27438728 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic Dissemination of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus after Penile Inoculation.J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):4093-4104. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02947-15. Print 2016 Apr. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26865706 Free PMC article.
-
Soap and water prophylaxis for limiting genital ulcer disease and HIV-1 infection in men in sub-Saharan Africa.Genitourin Med. 1993 Aug;69(4):297-300. doi: 10.1136/sti.69.4.297. Genitourin Med. 1993. PMID: 7721293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral administration of the nucleoside EFdA (4'-ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine) provides rapid suppression of HIV viremia in humanized mice and favorable pharmacokinetic properties in mice and the rhesus macaque.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jul;59(7):4190-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05036-14. Epub 2015 May 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25941222 Free PMC article.
-
HIV infection and immune defense of the penis.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2011 Mar;65(3):220-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00941.x. Epub 2011 Jan 9. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21214659 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Hidden Enemy Within: Uncovering the Secrets of HIV Tissues Reservoirs and Current mRNA Vaccine Development.Curr HIV Res. 2024;22(2):73-81. doi: 10.2174/011570162X301593240409072840. Curr HIV Res. 2024. PMID: 38639272 Review.
References
-
- UNAIDS . 2020. Global HIV & AIDS Statistics — 2020 fact sheet. https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet.
-
- Baeten JM, Kahle E, Lingappa JR, Coombs RW, Delany-Moretlwe S, Nakku-Joloba E, Mugo NR, Wald A, Corey L, Donnell D, Campbell MS, Mullins JI, Celum C, Partners in Prevention HSV/HIV Transmission Study Team . 2011. Genital HIV-1 RNA predicts risk of heterosexual HIV-1 transmission. Sci Transl Med 3: 77ra29. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001888 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dyer JR, Eron JJ, Hoffman IF, Kazembe P, Vernazza PL, Nkata E, Costello Daly C, Fiscus SA, Cohen MS. 1998. Association of CD4 cell depletion and elevated blood and seminal plasma human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA concentrations with genital ulcer disease in HIV-1-infected men in Malawi. J Infect Dis 177:224–227. doi:10.1086/517359 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
