Construction of diagnostic and prognostic models based on gene signatures of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by machine learning methods
- PMID: 37304552
- PMCID: PMC10248568
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-22-2700
Construction of diagnostic and prognostic models based on gene signatures of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by machine learning methods
Abstract
Background: Diagnostic models based on gene signatures of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) were constructed by random forest (RF) and artificial neural network (ANN) algorithms. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (Lasso)-Cox regression was used to select and build prognostic models based on gene signatures. This study contributes to the early diagnosis and treatment, prognosis, and molecular mechanisms associated with NPC.
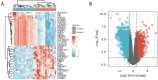
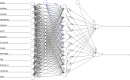
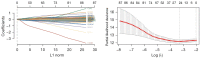
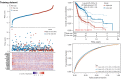
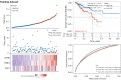
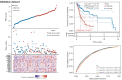
Methods: Two gene expression datasets were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with NPC were identified by gene expression differential analysis. Subsequently, significant DEGs were identified by a RF algorithm. ANN were used to construct a diagnostic model for NPC. The performance of the diagnostic model was evaluated by area under the curve (AUC) values using a validation set. Lasso-Cox regression examined gene signatures associated with prognosis. Overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) prediction models were constructed and validated from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and the International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) database.
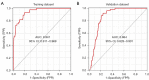
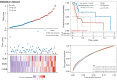
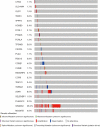
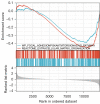
Results: A total of 582 DEGs associated with NPC were identified, and 14 significant genes were identified by the RF algorithm. A diagnostic model for NPC was successfully constructed using ANN, and the validity of the model was confirmed on the training set AUC =0.947 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.911-0.969] and the validation set AUC =0.864 (95% CI: 0.828-0.901). The 24-gene signatures associated with prognosis were identified by Lasso-Cox regression, and prediction models for OS and DFS of NPC were constructed on the training set. Finally, the ability of the model was validated on the validation set.
Conclusions: Several potential gene signatures associated with NPC were identified, and a high-performance predictive model for early diagnosis of NPC and a prognostic prediction model with robust performance were successfully developed. The results of this study provide valuable references for early diagnosis, screening, treatment and molecular mechanism research of NPC in the future.
Keywords: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC); bioinformatics; diagnostic model; disease markers; machine learning.
2023 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-22-2700/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Construction of Novel Gene Signature-Based Predictive Model for the Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction by Combining Random Forest With Artificial Neural Network.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 25;9:876543. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.876543. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35694667 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of ischemic stroke diagnosis models based on machine learning.Front Neurol. 2022 Dec 5;13:1014346. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1014346. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36545400 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a prognostic score model for breast cancer based on multi-omics analysis of study on bone metastasis.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 May 31;13(5):2419-2436. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1881. Epub 2024 May 20. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38881940 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning and deep learning methods that use omics data for metastasis prediction.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Sep 4;19:5008-5018. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.09.001. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34589181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using machine learning algorithms to predict the prognosis of advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma after intensity-modulated radiotherapy.Curr Probl Cancer. 2024 Feb;48:101040. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2023.101040. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Curr Probl Cancer. 2024. PMID: 37979476 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive accuracy of machine learning for radiation-induced temporal lobe injury in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 30;12(9):2361-2370. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-859. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37859745 Free PMC article.
-
A literature review: machine learning-based stem cell investigation.Ann Transl Med. 2024 Jun 10;12(3):52. doi: 10.21037/atm-23-1937. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Ann Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38911568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lam WKJ, Chan JYK. Recent advances in the management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. F1000Res 2018;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1829. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
