Exploring the Impact of Cyanidin-3-Glucoside on Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Investigating New Mechanisms for Emerging Interventions
- PMID: 37298350
- PMCID: PMC10254033
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119399
Exploring the Impact of Cyanidin-3-Glucoside on Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Investigating New Mechanisms for Emerging Interventions
Abstract
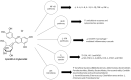
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (C3G), the most widely distributed anthocyanin (ACN) in edible fruits, has been proposed for several bioactivities, including anti-inflammatory, neuro-protective, antimicrobial, anti-viral, anti-thrombotic and epigenetic actions. However, habitual intake of ACNs and C3G may vary widely among populations, regions, and seasons, among individuals with different education and financial status. The main point of C3G absorption occurs in the small and large bowel. Therefore, it has been supposed that the treating properties of C3G might affect inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD). IBDs develop through complex inflammatory pathways and sometimes may be resistant to conventional treatment strategies. C3G presents antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective, and antimicrobial effects useful for IBD management. In particular, different studies have demonstrated that C3G inhibits NF-κB pathway activation. In addition, C3G activates the Nrf2 pathway. On the other hand, it modulates the expression of antioxidant enzymes and cytoprotective proteins, such as NAD(P)H, superoxide dismutase, heme-oxygenase (HO-1), thioredoxin, quinone reductase-oxide 1 (NQO1), catalase, glutathione S-transferase and glutathione peroxidase. Interferon I and II pathways are downregulated by C3G inhibiting interferon-mediating inflammatory cascades. Moreover, C3G reduces reactive species and pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as C reactive protein, interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-5, IL-9, IL-10, IL-12p70, and IL-17A in UC and CD patients. Finally, C3G modulates gut microbiota by inducing an increase in beneficial gut bacteria and increasing microbial abundances, thus mitigating dysbiosis. Thus, C3G presents activities that may have potential therapeutic and protective actions against IBD. Still, in the future, clinical trials should be designed to investigate the bioavailability of C3G in IBD patients and the proper therapeutic doses through different sources, aiming to the standardization of the exact clinical outcome and efficacy of C3G.
Keywords: C3G; Crohn’s disease; IBD; anthocyanin; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of Gut Microbial Metabolism by Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside in Mitigating Polystyrene-Induced Colonic Inflammation: Insights from 16S rRNA Sequencing and Metabolomics.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Apr 3;72(13):7140-7154. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c08454. Epub 2024 Mar 22. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38518253
-
Recent advances on cyanidin-3-O-glucoside in preventing obesity-related metabolic disorders: A comprehensive review.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Oct 15;729:150344. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150344. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38976946 Review.
-
Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside and Cyanidin Protect Against Intestinal Barrier Damage and 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzenesulfonic Acid-Induced Colitis.J Med Food. 2020 Jan;23(1):90-99. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2019.4524. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Med Food. 2020. PMID: 31657664
-
Combination of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside and cisplatin induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in HeLa cells by reducing activity of endogenous antioxidants, increasing bax/bcl-2 mRNA expression ratio, and downregulating Nrf2 expression.J Food Biochem. 2021 Jul;45(7):e13806. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13806. Epub 2021 Jun 2. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34080212
-
Health benefits of cyanidin-3-glucoside as a potent modulator of Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Aug;29(4):907-923. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00799-7. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33740221 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Role of an Anthocyanin, Cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside in Obesity-Related Complications.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 17;12(22):3889. doi: 10.3390/plants12223889. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Surviving Effect of Cleome droserifolia Extract against Systemic Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Investigation of the Chemical Content of the Plant.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 15;13(5):450. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050450. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martins I., Maciel M.G., do Nascimento J.L.M., Mafra D., Santos A.F., Padilha C.S. Anthocyanins-rich interventions on oxidative stress, inflammation and lipid profile in patients undergoing hemodialysis: Meta-analysis and meta-regression. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023;77:316–324. doi: 10.1038/s41430-022-01175-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

