Safety of Low-Dose Oral Food Challenges for Hen's Eggs, Cow's Milk, and Wheat: Report from a General Hospital without Allergy Specialists in Japan
- PMID: 37291068
- PMCID: PMC10306261
Safety of Low-Dose Oral Food Challenges for Hen's Eggs, Cow's Milk, and Wheat: Report from a General Hospital without Allergy Specialists in Japan
Abstract
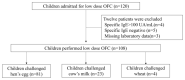
An oral food challenge (OFC) is useful for managing food allergies. However, because OFCs have the risk of severe allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, conducting OFCs under this situation without allergy specialists is difficult. To investigate the safety of a low-dose OFC for eggs, milk, and wheat in a general hospital without allergy specialists. We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of children who were hospitalized in a general hospital without allergy specialists for a low-dose OFC of egg, milk, or wheat between April 2018 and March 2021. The records of 108 patients were evaluated. The median age was 15.8 months (range: 7.5-69.3 months). Challenged foods were eggs (n = 81), milk (n = 23), and wheat (n = 4). Fifty-three (49.0%) patients showed positive allergic reactions. Thirty-five (66.0%) patients showed grade 1 (mild), 18 (34.0%) showed grade 2 (moderate), and none showed grade 3 (severe) reactions. The interventions comprised antihistamines (n = 18), prednisolone (n = 3), inhaled Β2-agonist (n = 2). No patients required adrenaline and no deaths occurred. Low-dose OFCs may be safe in a general hospital without allergy specialists. Conducting a low-dose OFC may be essential in food allergy practice.
Keywords: Anaphylaxis; Food allergy; Food hypersensitivity; Guidelines; Safety.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low-dose oral food challenges.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2024 Oct;35(10):e14258. doi: 10.1111/pai.14258. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39396116
-
Oral food challenge in IgE mediated food allergy in eastern Mediterranean children.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021 May 1;49(3):185-192. doi: 10.15586/aei.v49i3.189. eCollection 2021. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021. PMID: 33938205
-
Is oral food challenge test useful for avoiding complete elimination of cow's milk in Japanese patients with or suspected of having IgE-dependent cow's milk allergy?Allergol Int. 2022 Apr;71(2):214-220. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2021.09.001. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Allergol Int. 2022. PMID: 34593320
-
Types and Amounts of Complementary Foods and Beverages and Food Allergy, Atopic Dermatitis/Eczema, Asthma, and Allergic Rhinitis: A Systematic Review [Internet].Alexandria (VA): USDA Nutrition Evidence Systematic Review; 2019 Apr. Alexandria (VA): USDA Nutrition Evidence Systematic Review; 2019 Apr. PMID: 35816599 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Maternal Diet during Pregnancy and Lactation and Risk of Child Food Allergies and Atopic Allergic Diseases: A Systematic Review [Internet].Alexandria (VA): USDA Nutrition Evidence Systematic Review; 2020 Jul. Alexandria (VA): USDA Nutrition Evidence Systematic Review; 2020 Jul. PMID: 35289989 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Ebisawa M, Sugizaki C. Prevalence Of Pediatric Allergic Diseases In The First 5 Years Of Life. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121(2):S237.
-
- Sicherer SH, Muñoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Prevalence of seafood allergy in the United States determined by a random telephone survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114(1):159–65. - PubMed
-
- Ebisawa M, Ito K, Fujisawa T. Japanese guidelines for food allergy 2020. Allergol Int. 2020;69(3):370–86. - PubMed
-
- Bird JA, Leonard S, Groetch M, Assa’ad A, Cianferoni A, Clark A, et al. Conducting an Oral Food Challenge: An Update to the 2009 Adverse Reactions to Foods Committee Work Group Report. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8(1):75–90e17. - PubMed
-
- Yanagida N, Minoura T, Kitaoka S, Ebisawa M. A three-level stepwise oral food challenge for egg, milk, and wheat allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6(2):658–60e10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous