Assessment of eight insulin resistance surrogate indexes for predicting metabolic syndrome and hypertension in Thai law enforcement officers
- PMID: 37273533
- PMCID: PMC10234272
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15463
Assessment of eight insulin resistance surrogate indexes for predicting metabolic syndrome and hypertension in Thai law enforcement officers
Abstract
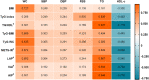
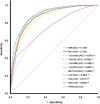
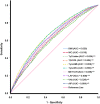
Police officers in Thailand have an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes, possibly due to a high prevalence of hypertension and metabolic syndrome (MetS). In this study, the researchers aimed to understand the relationship between surrogate markers of insulin resistance (IR) and the prevalence of MetS and hypertension in Thai police officers. The study included 7,852 police officer participants, of which 91.8% were men with an average age of 48.56 years. The prevalence of hypertension and MetS were found to be 51.1% and 30.8%, respectively, and the participants with MetS and hypertension were older compared to the regular group. The study looked at eight IR indices, including markers such as atherogenic index of plasma (AIP), lipid accumulation product (LAP), metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR), triglyceride glucose (TyG) index, TyG index with body mass index (TyG-BMI), TyG index with waist circumference (TyG-WC), the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (TG/HDL-c), and visceral obesity index (VAI). These indices were found to be positively correlated with waist circumference, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and triglycerides (TG), while being negatively correlated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c). In addition, the multiple regression analysis showed that higher quartiles of all IR indices were significantly associated with increased risks of MetS and hypertension. Interestingly, the IR indices were more accurate in predicting MetS (ranges 0.848 to 0.892) than traditional obesity indices, with the AUC difference at p < 0.001. Among the IR indices, TyG-WC performed the best in predicting MetS (AUC value 0.892 and Youden index 0.620). At the same time, TyG-BMI had the highest accuracy in predicting hypertension (AUC value of 0.659 and Youden index of 0.236). In addition, this study found that when two markers were combined for diagnosing metabolic syndrome, a significantly improved predictive value for disease risk was observed, as evidenced by higher AUC and Yoden index. Moreover, the IR indices were found to have higher predictive power for MetS and hypertension in younger police personnel (age < 48 years) than older personnel. In conclusion, this study highlights the importance of reducing cardiovascular disease risks among law enforcement personnel as a strategic goal to improve their health and wellness. The findings suggest that IR indices may be valuable tools in predicting MetS and hypertension in law enforcement personnel and could potentially aid in the early identification and prevention of law enforcement personnel health conditions.
Keywords: Hypertension; Insulin resistance surrogate index; Law enforcement officer; Metabolic syndrome; Police officer.
© 2023 Rattanatham et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Associations Between Insulin Resistance Indexes and Hyperuricemia in Hypertensive Population].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2023 Jun;45(3):390-398. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.15414. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37407524 Chinese.
-
Obesity- and lipid-related indices as a predictor of obesity metabolic syndrome in a national cohort study.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 14;11:1073824. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1073824. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36875382 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of measuring anthropometric and atherogenic indices in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Aug 28;24(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01701-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39198818 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of walnut consumption on cardio metabolic and anthropometric parameters in metabolic syndrome patients: GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of data from randomized controlled trials.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Apr;178:106190. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106190. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 35338001 Review.
-
Assessment of preferred methods to measure insulin resistance in Asian patients with hypertension.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021 Mar;23(3):529-537. doi: 10.1111/jch.14155. Epub 2021 Jan 7. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021. PMID: 33415834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of atherogenic indices for predicting the risk of metabolic syndrome in Southwest Iran: results from the Hoveyzeh Cohort Study (HCS).Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 May 23;16(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01349-1. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38783371 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship of triglyceride-glucose index and its derivatives with blood pressure abnormalities in adolescents: an analysis based on a restricted cubic spline model].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jan 15;26(1):54-61. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2306049. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38269460 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Iron Homeostasis-Related Parameters and Hepcidin/Ferritin Ratio: Emerging Sex-Specific Predictive Markers for Metabolic Syndrome.Metabolites. 2024 Aug 28;14(9):473. doi: 10.3390/metabo14090473. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39330480 Free PMC article.
-
Negative correlation between metabolic score for insulin resistance index and testosterone in male adults.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 May 23;16(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01353-5. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38783379 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Resistance Surrogates May Predict HTN-HUA in Young, Non-Obese Individuals.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Sep 28;17:3593-3601. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S482184. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39360017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbasi F, Reaven GM. Comparison of two methods using plasma triglyceride concentration as a surrogate estimate of insulin action in nondiabetic subjects: triglycerides × glucose versus triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Metabolism-clinical and Experimental. 2011;60(12):1673–1676. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.04.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aekplakorn W, Puckcharern H, Satheannoppakao W. The National Health Examination Survey of Thailand 2019–2020. Bangkok: Aksorn Graphic and Design Publishing; 2021.
-
- Ahn N, Baumeister SE, Amann U, Rathmann W, Peters A, Huth C, Thorand B, Meisinger C. Visceral adiposity index (VAI), lipid accumulation product (LAP), and product of triglycerides and glucose (TyG) to discriminate prediabetes and diabetes. Scientific Reports. 2019;9(1):9693. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46187-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aslan Çin NN, Yardımcı H, Koç N, Uçaktürk SA, Akçil Ok M. Triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a predictor similar to the triglyceride-glucose index for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome using International Diabetes Federation criteria of insulin resistance in obese adolescents: a cross-sectional study. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2020;33(6):777–784. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2019-0310. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barrett BJ, Fardy JM. Evaluation of diagnostic tests. In: Parfrey PS, Barrett BJ, editors. Clinical Epidemiology: Practice and Methods. New York, NY: Springer US; 2021. pp. 319–333.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

