The Arabidopsis thaliana onset of leaf death 12 mutation in the lectin receptor kinase P2K2 results in an autoimmune phenotype
- PMID: 37264342
- PMCID: PMC10236711
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-023-04300-0
The Arabidopsis thaliana onset of leaf death 12 mutation in the lectin receptor kinase P2K2 results in an autoimmune phenotype
Abstract
Background: Plant immunity relies on the perception of immunogenic signals by cell-surface and intracellular receptors and subsequent activation of defense responses like programmed cell death. Under certain circumstances, the fine-tuned innate immune system of plants results in the activation of autoimmune responses that cause constitutive defense responses and spontaneous cell death in the absence of pathogens.
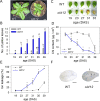
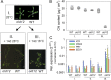
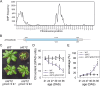
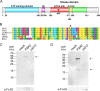
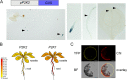
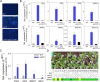
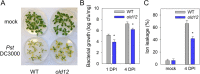
Results: Here, we characterized the onset of leaf death 12 (old12) mutant that was identified in the Arabidopsis accession Landsberg erecta. The old12 mutant is characterized by a growth defect, spontaneous cell death, plant-defense gene activation, and early senescence. In addition, the old12 phenotype is temperature reversible, thereby exhibiting all characteristics of an autoimmune mutant. Mapping the mutated locus revealed that the old12 phenotype is caused by a mutation in the Lectin Receptor Kinase P2-TYPE PURINERGIC RECEPTOR 2 (P2K2) gene. Interestingly, the P2K2 allele from Landsberg erecta is conserved among Brassicaceae. P2K2 has been implicated in pathogen tolerance and sensing extracellular ATP. The constitutive activation of defense responses in old12 results in improved resistance against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that old12 is an auto-immune mutant and that allelic variation of P2K2 contributes to diversity in Arabidopsis immune responses.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; Autoimmunity; Onset of leaf death; Receptor-like kinase; Salicylic acid.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis Lectin Receptor Kinase P2K2 Is a Second Plant Receptor for Extracellular ATP and Contributes to Innate Immunity.Plant Physiol. 2020 Jul;183(3):1364-1375. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.01265. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32345768 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.9 is required for full resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and affects jasmonate signalling.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Sep;18(7):937-948. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12457. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27399963 Free PMC article.
-
A salicylic acid-induced lectin-like protein plays a positive role in the effector-triggered immunity response of Arabidopsis thaliana to Pseudomonas syringae Avr-Rpm1.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013 Dec;26(12):1395-406. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-13-0044-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013. PMID: 24006883
-
The Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinase LecRK-V.5 represses stomatal immunity induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Feb;8(2):e1002513. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002513. Epub 2012 Feb 9. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22346749 Free PMC article.
-
IDL6-HAE/HSL2 impacts pectin degradation and resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato DC3000 in Arabidopsis leaves.Plant J. 2017 Jan;89(2):250-263. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13380. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 27618493
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

