Gut microbiota derived bile acid metabolites maintain the homeostasis of gut and systemic immunity
- PMID: 37256134
- PMCID: PMC10225537
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127743
Gut microbiota derived bile acid metabolites maintain the homeostasis of gut and systemic immunity
Abstract
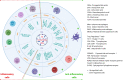
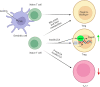
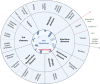
Bile acids (BAs) as cholesterol-derived molecules play an essential role in some physiological processes such as nutrient absorption, glucose homeostasis and regulation of energy expenditure. They are synthesized in the liver as primary BAs such as cholic acid (CA), chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and conjugated forms. A variety of secondary BAs such as deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA) and their derivatives is synthesized in the intestine through the involvement of various microorganisms. In addition to essential physiological functions, BAs and their metabolites are also involved in the differentiation and functions of innate and adaptive immune cells such as macrophages (Macs), dendritic cells (DCs), myeloid derived suppressive cells (MDSCs), regulatory T cells (Treg), Breg cells, T helper (Th)17 cells, CD4 Th1 and Th2 cells, CD8 cells, B cells and NKT cells. Dysregulation of the BAs and their metabolites also affects development of some diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases. We here summarize recent advances in how BAs and their metabolites maintain gut and systemic homeostasis, including the metabolism of the BAs and their derivatives, the role of BAs and their metabolites in the differentiation and function of immune cells, and the effects of BAs and their metabolites on immune-associated disorders.
Keywords: bile acids; deoxycholic acid; gut microbiota; lithocholic acid; regulatory B cells; regulatory T cells; tolerogenic macrophages.
Copyright © 2023 Su, Gao and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gut-Microbiota-Derived Metabolites Maintain Gut and Systemic Immune Homeostasis.Cells. 2023 Mar 2;12(5):793. doi: 10.3390/cells12050793. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strain-dependent induction of primary bile acid 7-dehydroxylation by cholic acid.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Aug 1;24(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03433-y. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39090543 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acid coordinates microbiota homeostasis and systemic immunometabolism in cardiometabolic diseases.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 May;12(5):2129-2149. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.12.011. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35646540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative profiling of 19 bile acids in rat plasma, liver, bile and different intestinal section contents to investigate bile acid homeostasis and the application of temporal variation of endogenous bile acids.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Sep;172:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.05.015. Epub 2017 Jun 3. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28583875
-
The influences of cholecystectomy on the circadian rhythms of bile acids as well as the enterohepatic transporters and enzymes systems in mice.Chronobiol Int. 2018 May;35(5):673-690. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2018.1426596. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Chronobiol Int. 2018. PMID: 29381405
Cited by
-
Insights into the liver-eyes connections, from epidemiological, mechanical studies to clinical translation.J Transl Med. 2023 Oct 10;21(1):712. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04543-3. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37817192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Clues to Bile Acid Patterns and Prolonged Survival in Patients with Metastatic Soft-Tissue Sarcoma Treated with Trabectedin.Metabolites. 2023 Sep 26;13(10):1035. doi: 10.3390/metabo13101035. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37887360 Free PMC article.
-
Houttuynia cordata thunb. alleviates inflammatory bowel disease by modulating intestinal microenvironment: a research review.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 22;14:1306375. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1306375. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38077358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction on the regulation of gut microbiota and metabolites in type II diabetic rats.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1429360. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1429360. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39234553 Free PMC article.
-
Oral treatment of human gut microbiota associated IL-10-/- mice suffering from acute campylobacteriosis with carvacrol, deferoxamine, deoxycholic acid, and 2-fucosyl-lactose.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 25;15:1290490. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1290490. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38343716 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

