Progress in the Prevalence, Classification and Drug Resistance Mechanisms of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 37255882
- PMCID: PMC10226514
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S412308
Progress in the Prevalence, Classification and Drug Resistance Mechanisms of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
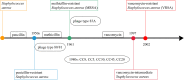
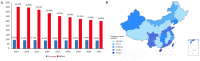
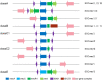
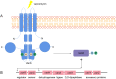
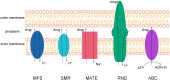
Staphylococcus aureus is a common human pathogen with a variety of virulence factors, which can cause multiple infectious diseases. In recent decades, due to the constant evolution and the abuse of antibiotics, Staphylococcus aureus was becoming more resistant, the infection rate of MRSA remained high, and clinical treatment of MRSA became more difficult. The genetic diversity of MRSA was mainly represented by the continuous emergence of epidemic strains, resulting in the constant changes of epidemic clones. Different classes of MRSA resulted in different epidemics and resistance characteristics, which could affect the clinical symptoms and treatments. MRSA had also spread from traditional hospitals to community and livestock environments, and the new clones established a relationship between animals and humans, promoting further evolution of MRSA. Since the resistance mechanism of MRSA is very complex, it is important to clarify these resistance mechanisms at the molecular level for the treatment of infectious diseases. We firstly described the diversity of SCCmec elements, and discussed the types of SCCmec, its drug resistance mechanisms and expression regulations. Then, we described how the vanA operon makes Staphylococcus aureus resistant to vancomycin and its expression regulation. Finally, a brief introduction was given to the drug resistance mechanisms of biofilms and efflux pump systems. Analyzing the resistance mechanism of MRSA can help study new anti-infective drugs and alleviate the evolution of MRSA. At the end of the review, we summarized the treatment strategies for MRSA infection, including antibiotics, anti-biofilm agents and efflux pump inhibitors. To sum up, here we reviewed the epidemic characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus, summarized its classifications, drug resistance mechanisms of MRSA (SCCmec element, vanA operon, biofilm and active efflux pump system) and novel therapy strategies, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the treatment of MRSA infection.
Keywords: MRSA; SCCmec; biofilm; efflux pump; prevalence; resistance mechanism.
© 2023 Hou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New update on molecular diversity of clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Iran: antimicrobial resistance, adhesion and virulence factors, biofilm formation and SCCmec typing.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Apr;49(4):3099-3111. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07140-7. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35064407
-
Genetic diversity of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from burn patients in Iran: ST239-SCCmec III/t037 emerges as the major clone.Microb Pathog. 2017 Apr;105:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Feb 5. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28179118
-
Clinical and Molecular Epidemiology of an Emerging Panton-Valentine Leukocidin-Positive ST5 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clone in Northern Australia.mSphere. 2021 Feb 10;6(1):e00651-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00651-20. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 33568451 Free PMC article.
-
Bridges from hospitals to the laboratory: genetic portraits of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004 Mar 8;40(2):101-11. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00370-5. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15040388 Review.
-
Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Mar 17;10:107. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00107. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32257966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence, drug resistance, molecular typing and comparative genomics analysis of MRSA strains from a tertiary A hospital in Shanxi Province, China.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 22;14:1273397. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1273397. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37808303 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on Staphylococcus aureus infections in pediatric patients admitted with community acquired pneumonia.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 8;14(1):15737. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66071-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38977804 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design, synthesis, molecular modeling, biological activity, and mechanism of action of polypharmacological norfloxacin hydroxamic acid derivatives.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Sep 19;14(12):2593-2610. doi: 10.1039/d3md00309d. eCollection 2023 Dec 13. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 38099058 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Dairy Products and Bulk-Tank Milk (BTM).Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jun 25;13(7):588. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070588. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug repurposing: insights into the antimicrobial effects of AKBA against MRSA.AMB Express. 2024 Jan 6;14(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13568-024-01660-0. AMB Express. 2024. PMID: 38184513 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

