Prophylactic cranial irradiation-related lymphopenia affects survival in patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 37251477
- PMCID: PMC10220366
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16483
Prophylactic cranial irradiation-related lymphopenia affects survival in patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The study aimed to identify the relations of the absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) nadir during prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) and patient outcomes in limited-stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC).
Methods: We analyzed 268 L S-SCLC patients who underwent PCI from 2012 to 2019. ALC values were collected prior, during, and 3 months post PCI. Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses were performed to assess the relation of ALC to patient prognosis. Two nomograms were developed on the basis of clinical variables for survival prediction.
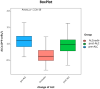
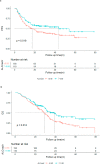
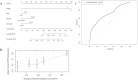
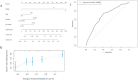
Results: Compared with the ALC before PCI (1.13 × 109 cells/L), the ALC nadir during PCI was significantly reduced by 0.68 × 109 cells/L (P < 0.001) and raised to 1.02 × 109 cells/L 3 months post PCI. Patients with a low ALC nadir during PCI (<0.68 × 109 cells/L) had inferior progression free survival (PFS) (median PFS: 17.2 m vs. 43.7 m, P = 0.019) and overall survival (OS) (median OS: 29.0 m vs 39.1 m, P = 0.012). Multivariate Cox analysis revealed that age, smoking history, clinical stage, and ALC nadir were independent OS (P = 0.006, P = 0.005, P < 0.001 and P = 0.027, respectively), as well as independent PFS predictors (P = 0.032, P = 0.012, P = 0.012 and P = 0.018, respectively). After internal cross-validation, the corrected concordance indices of the predictive nomograms for PFS and OS were 0.637 and 0.663, respectively.
Conclusion: LS-SCLC patients with a low ALC nadir during PCI likely have worse survival outcomes. Dynamic evaluation of the ALC during PCI is recommended for LS-SCLC patients.
Keywords: Limited-stage small-cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC); Lymphopenia; Overall survival (OS); Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI).
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lymphopenia association with accelerated hyperfractionation and its effects on limited-stage small cell lung cancer patients' clinical outcomes.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Aug;7(16):385. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.07.58. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31555699 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of prophylactic cranial irradiation in patients with small cell lung cancer in the modern era of baseline magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.Acta Oncol. 2022 Feb;61(2):185-192. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2021.1974553. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Acta Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34583620
-
Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: Is Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Necessary?Pract Radiat Oncol. 2019 Nov;9(6):e599-e607. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2019.06.014. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31271904
-
Should Stereotactic Radiosurgery Be Considered for Salvage of Intracranial Recurrence after Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation or Whole Brain Radiotherapy in Small Cell Lung Cancer? A Population-Based Analysis and Literature Review.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2020 Mar;51(1):75-87.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2019.10.001. Epub 2019 Nov 20. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2020. PMID: 31759940 Review.
-
The overall survival impact of prophylactic cranial irradiation in limited-stage small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2022 Feb 17;33:145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2022.02.002. eCollection 2022 Mar. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35243025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Meerbeeck J.P., Fennell D.A., De Ruysscher D.K. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 2011;378:1741–1755. - PubMed
-
- Govindan R., Page N., Morgensztern D., et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:4539–4544. - PubMed
-
- Wang S., Zimmermann S., Parikh K., et al. Current diagnosis and management of small-cell lung cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019;94:1599–1622. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

