Mitochondrial Replication Assay (MIRA) for Efficient in situ Quantification of Nascent mtDNA and Protein Interactions with Nascent mtDNA (mitoSIRF)
- PMID: 37251092
- PMCID: PMC10213078
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4680
Mitochondrial Replication Assay (MIRA) for Efficient in situ Quantification of Nascent mtDNA and Protein Interactions with Nascent mtDNA (mitoSIRF)
Abstract
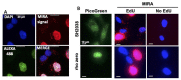
Mitochondria play decisive roles in bioenergetics and intracellular communication. These organelles contain a circular mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) genome that is duplicated within one to two hours by a mitochondrial replisome, independently from the nuclear replisome. mtDNA stability is regulated in part at the level of mtDNA replication. Consequently, mutations in mitochondrial replisome components result in mtDNA instability and are associated with diverse disease phenotypes, including premature aging, aberrant cellular energetics, and developmental defects. The mechanisms ensuring mtDNA replication stability are not completely understood. Thus, there remains a need to develop tools to specifically and quantifiably examine mtDNA replication. To date, methods for labeling mtDNA have relied on prolonged exposures of 5'-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU) or 5'-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU). However, labeling with these nucleoside analogs for a sufficiently short time in order to monitor nascent mtDNA replication, such as under two hours, does not produce signals suited for efficient or accurate quantitative analysis. The assay system described here, termed Mitochondrial Replication Assay (MIRA), utilizes proximity ligation assay (PLA) combined with EdU-coupled Click-IT chemistry to address this limitation, thereby enabling sensitive and quantitative analysis of nascent in situ mtDNA replication with single-cell resolution. This method can be further paired with conventional immunofluorescence (IF) for multi-parameter cell analysis. By enabling monitoring nascent mtDNA prior to the complete replication of the entire mtDNA genome, this new assay system allowed the discovery of a new mitochondrial stability pathway, mtDNA fork protection. Moreover, a modification in primary antibodies application allows the adaptation of our previously described in situ protein Interactions with nascent DNA Replication Forks (SIRF) for the detection of proteins of interest to nascent mtDNA replication forks on a single molecule level (mitoSIRF). Graphical overview Schematic overview of Mitochondrial Replication Assay (MIRA). 5'-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU; green) incorporated in DNA is tagged with biotin (blue) using Click-IT chemistry. Subsequent proximity ligation assay (PLA, pink circles) using antibodies against biotin allows the fluorescent tagging of the nascent EdU and amplification of the signal sufficient for visualization by standard immunofluorescence. PLA signals outside the nucleus denote mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) signals. Ab, antibody. In in situ protein interactions with nascent DNA replication forks (mitoSIRF), one of the primary antibodies is directed against a protein of interest, while the other detects nascent biotinylated EdU, thus enabling in situ protein interactions with nascent mtDNA.
Keywords: BRCA2; Fanconi anemia; MIRA; Mitochondria; Mitochondrial DNA; Proximity ligation assay; mtDNA instability; mtDNA replication.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SIRF: A Single-cell Assay for in situ Protein Interaction with Nascent DNA Replication Forks.Bio Protoc. 2019 Sep 20;9(18):e3377. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3377. eCollection 2019 Sep 20. Bio Protoc. 2019. PMID: 33654873 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Analysis of Histone Acetylation Dynamics at Replication Forks Using PLA and SIRF.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2589:345-360. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2788-4_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36255636
-
Detection and Quantitation of Acetylated Histones on Replicating DNA Using In Situ Proximity Ligation Assay and Click-It Chemistry.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1983:29-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9434-2_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31087291 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA replication: clinical syndromes.Essays Biochem. 2018 Jul 20;62(3):297-308. doi: 10.1042/EBC20170101. Print 2018 Jul 20. Essays Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29950321 Review.
-
Mitochondrial DNA replication and repair defects: Clinical phenotypes and therapeutic interventions.Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2022 Jun 1;1863(5):148554. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2022.148554. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2022. PMID: 35341749 Review.
References
-
- Chatterjee A., Mambo E. and Sidransky D.(2006). Mitochondrial DNA mutations in human cancer. Oncogene 25(34): 4663-4674. - PubMed
-
- Clayton D. A.(1982). Replication of animal mitochondrial DNA. Cell 28(4): 693-705. - PubMed
-
- Falkenberg M., Larsson N. G. and Gustafsson C. M.(2007). DNA replication and transcription in mammalian mitochondria. Annu Rev Biochem 76: 679-699. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

