Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption and Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Microbial and Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers
- PMID: 37242931
- PMCID: PMC10222159
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15102356
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption and Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Microbial and Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers
Abstract
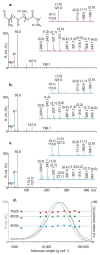
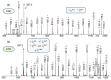
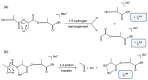
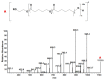
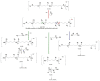
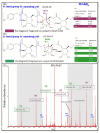
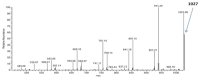
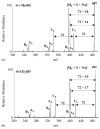
The in-depth structural and compositional investigation of biodegradable polymeric materials, neat or partly degraded, is crucial for their successful applications. Obviously, an exhaustive structural analysis of all synthetic macromolecules is essential in polymer chemistry to confirm the accomplishment of a preparation procedure, identify degradation products originating from side reactions, and monitor chemical-physical properties. Advanced mass spectrometry (MS) techniques have been increasingly applied in biodegradable polymer studies with a relevant role in their further development, valuation, and extension of application fields. However, single-stage MS is not always sufficient to identify unambiguously the polymer structure. Thus, tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) has more recently been employed for detailed structure characterization and in degradation and drug release monitoring of polymeric samples, among which are biodegradable polymers. This review aims to run through the investigations carried out by the soft ionization technique matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) MS/MS in biodegradable polymers and present the resulting information.
Keywords: ESI; MALDI; biodegradable polymers; characterization; degradation; drug delivery systems; multi stage mass spectrometry; tandem mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modern mass spectrometry in the characterization and degradation of biodegradable polymers.Anal Chim Acta. 2014 Jan 15;808:18-43. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Anal Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24370091 Review.
-
"Polymeromics": Mass spectrometry based strategies in polymer science toward complete sequencing approaches: a review.Anal Chim Acta. 2014 Jan 15;808:56-69. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.10.027. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Anal Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24370093 Review.
-
Tandem mass spectrometry of synthetic polymers.J Mass Spectrom. 2009 Sep;44(9):1277-86. doi: 10.1002/jms.1623. J Mass Spectrom. 2009. PMID: 19676098
-
Characteristics of glycation and glycation sites of lysozyme by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight/time-of-flight mass spectrometry and Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry.Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2014;20(4):327-36. Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2014. PMID: 25420345
-
Tandem mass spectrometry of poly(ethylene imine)s by electrospray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI).J Mass Spectrom. 2012 Jan;47(1):105-14. doi: 10.1002/jms.2032. J Mass Spectrom. 2012. PMID: 22282096
Cited by
-
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Production from Lignocellulosic Wastes Using Bacillus megaterium ATCC 14581.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Nov 22;15(23):4488. doi: 10.3390/polym15234488. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38231921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalita N.K., Hakkarainen M. Integrating biodegradable polyesters in a circular economy. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023;40:100751. doi: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2022.100751. - DOI
-
- Li X., Lin Y., Liu M., Meng L., Li C. A review of research and application of polylactic acid composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023;140:e53477. doi: 10.1002/app.53477. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

