Therapeutic Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles for Regenerative Medicine
- PMID: 37242627
- PMCID: PMC10222259
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051385
Therapeutic Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles for Regenerative Medicine
Abstract
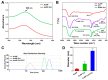
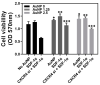
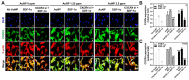
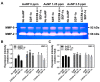
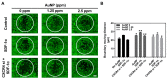
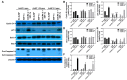
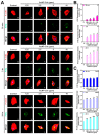
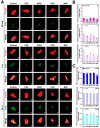
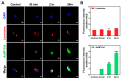
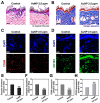
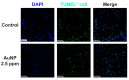
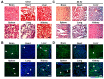
In the present study, the various concentrations of AuNP (1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 ppm) were prepared to investigate the biocompatibility, biological performances and cell uptake efficiency via Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells and rat model. The pure AuNP, AuNP combined with Col (AuNP-Col) and FITC conjugated AuNP-Col (AuNP-Col-FITC) were characterized by Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) assays. For in vitro examinations, we explored whether the Wharton's jelly MSCs had better viability, higher CXCR4 expression, greater migration distance and lower apoptotic-related proteins expression with AuNP 1.25 and 2.5 ppm treatments. Furthermore, we considered whether the treatments of 1.25 and 2.5 ppm AuNP could induce the CXCR4 knocked down Wharton's jelly MSCs to express CXCR4 and reduce the expression level of apoptotic proteins. We also treated the Wharton's jelly MSCs with AuNP-Col to investigate the intracellular uptake mechanisms. The evidence demonstrated the cells uptake AuNP-Col through clathrin-mediated endocytosis and the vacuolar-type H+-ATPase pathway with good stability inside the cells to avoid lysosomal degradation as well as better uptake efficiency. Additionally, the results from in vivo examinations elucidated the 2.5 ppm of AuNP attenuated foreign body responses and had better retention efficacy with tissue integrity in animal model. In conclusion, the evidence demonstrates that AuNP shows promise as a biosafe nanodrug delivery system for development of regenerative medicine coupled with Wharton's jelly MSCs.
Keywords: biological performance; gold nanoparticle; mesenchymal stem cell; nanodrug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Favorable Biological Performance Regarding the Interaction between Gold Nanoparticles and Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 20;24(1):5. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010005. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613448 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Feline Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Vet Sci. 2021 Feb 7;8(2):24. doi: 10.3390/vetsci8020024. Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33562192 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of canine Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Transplant. 2012;21(7):1493-502. doi: 10.3727/096368912X647207. Cell Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22732242
-
Human Wharton's Jelly-Cellular Specificity, Stemness Potency, Animal Models, and Current Application in Human Clinical Trials.J Clin Med. 2020 Apr 12;9(4):1102. doi: 10.3390/jcm9041102. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32290584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wharton's jelly-derived stromal cells and their cell therapy applications in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Mar;26(5):1339-1350. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17105. Epub 2022 Jan 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35088933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precision Nanomedicine with Bio-Inspired Nanosystems: Recent Trends and Challenges in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Membrane-Coated Bioengineered Nanocarriers in Targeted Nanotherapeutics.J Xenobiot. 2024 Jun 24;14(3):827-872. doi: 10.3390/jox14030047. J Xenobiot. 2024. PMID: 39051343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo biocompatibility testing of nanoparticle-functionalized alginate-chitosan scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Nov 23;11:1295626. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1295626. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38076436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xue X., Hu Y., Deng Y., Su J. Recent advances in design of functional biocompatible hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2009432. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202009432. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

