Development and evaluation of pH sensitive semi-interpenetrating networks: assessing the impact of itaconic acid and aloe vera on network swelling and cetirizine release
- PMID: 37229490
- PMCID: PMC10203566
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1173883
Development and evaluation of pH sensitive semi-interpenetrating networks: assessing the impact of itaconic acid and aloe vera on network swelling and cetirizine release
Abstract
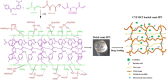
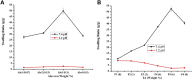
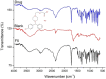
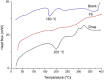
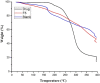
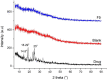
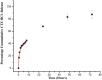
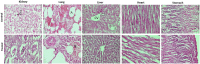
Hydrogels are crosslinked three-dimensional networks, and their properties can be easily tuned to target the various segments of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Cetirizine HCl (CTZ HCl) is an antihistaminic drug, which when given orally can upset the stomach. Moreover, this molecule has shown maximum absorption in the intestine. To address these issues, we developed a pH-responsive semi-interpenetrating polymer network (semi-IPN) for the delivery of CTZ HCl to the lower part of the GIT. Initially, 10 different formulations of itaconic acid-grafted-poly (acrylamide)/aloe vera [IA-g-poly (AAm)/aloe vera] semi-IPN were developed by varying the concentration of IA and aloe vera using the free radical polymerization technique. Based on swelling and sol-gel analysis, formulation F5 containing 0.3%w/w aloe vera and 6%w/w IA was chosen as the optimum formulation. The solid-state characterization of the optimized formulation (F5) revealed a successful incorporation of CTZ HCl in semi-IPN without any drug-destabilizing interaction. The in vitro drug release from F5 showed limited release in acidic media followed by a controlled release in the intestinal environment for over 72 h. Furthermore, during the in vivo evaluation, formulation F5 did not affect the hematological parameters, kidney, and liver functions. Clinical observations did not reveal any signs of illness in rabbits treated with hydrogels. Histopathological images of vital organs of treated animals showed normal cellular architecture. Thus, the results suggest a non-toxic nature and overall potential of the developed formulation as a targeted drug carrier.
Keywords: aloe vera; itaconic acid; pH sensitive; semi-interpenetrating network; sustainability of natural resources.
Copyright © 2023 Ajaz, Bukhsh, Kamal, Rehman, Irfan, Khalid, Asghar, Rizg, Bukhary, Hosny, Alissa, Safhi, Sabei and Khan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Optimization, in vitro release and toxicity evaluation of novel pH sensitive itaconic acid-g-poly(acrylamide)/sterculia gum semi-interpenetrating networks.Daru. 2021 Jun;29(1):171-184. doi: 10.1007/s40199-021-00395-8. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Daru. 2021. PMID: 33899162 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin-grafted-poly(acrylic acid)/poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) Semi-Interpenetrating Matrices of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 14;15(11):1399. doi: 10.3390/ph15111399. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422529 Free PMC article.
-
Aloe vera-Based Polymeric Network: A Promising Approach for Sustained Drug Delivery, Development, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation.Gels. 2023 Jun 8;9(6):474. doi: 10.3390/gels9060474. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37367144 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical approaches to colon targeted drug delivery systems.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2003 Jan-Apr;6(1):33-66. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2003. PMID: 12753729 Review.
-
Controlled release of therapeutics using interpenetrating polymeric networks.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Apr;12(4):669-88. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.974871. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25341410 Review.
Cited by
-
Chitosan/aloe vera gel coatings infused with orange peel essential oils for fruits preservation.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Feb 1;8:100680. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100680. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38328465 Free PMC article.
-
Development, Characterization, and Evaluation of Potential Systemic Toxicity of a Novel Oral Melatonin Formulation.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 28;16(7):871. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070871. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065568 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan in Oral Drug Delivery Formulations: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 21;15(9):2361. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092361. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765329 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afzal S., Khan S., Ranjha N. M., Jalil A., Riaz A., Haider M. S., et al. (2018). The structural, crystallinity, and thermal properties of pH-responsive interpenetrating gelatin/sodium alginate-based polymeric composites for the controlled delivery of cetirizine HCl. Turkish J. Pharm. Sci. 15 (1), 63–76. 10.4274/tjps.64326 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S., Usman Minhas M., Ahmad M., Sohail M., Abdullah O., Khan K. U. (2018). Topical hydrogel patches of vinyl monomers containing mupirocin for skin injuries: Synthesis and evaluation. Adv. Polym. Technol. 37, 3401–3411. 10.1002/adv.22124 - DOI
-
- Ajaz N., Khan I. U., Asghar S., Khalid S. H., Irfan M., Asif M., et al. (2021). Assessing the pH responsive and mucoadhesive behavior of dexamethasone sodium phosphate loaded itaconic acid-grafted-poly(acrylamide)/carbopol semi-interpenetrating networks. J. Polym. Res. 28 (8), 278. 10.1007/s10965-021-02643-6 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

