Increased expression of cell adhesion molecules in myofasciitis
- PMID: 37228411
- PMCID: PMC10203699
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1113404
Increased expression of cell adhesion molecules in myofasciitis
Abstract
Background: Myofasciitis is a heterogeneous group of diseases pathologically characterized by inflammatory cell infiltration into the fascia. Endothelial activation plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory response. However, the expression of cellular adhesion molecules (CAMs) in myofasciitis has not been investigated.
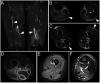
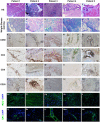
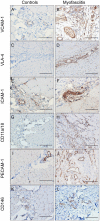
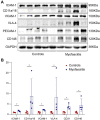
Methods: Data on clinical features, thigh magnetic resonance imaging, and muscle pathology were collected from five patients with myofasciitis. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining and Western blot (WB) of the muscle biopsies from patients and healthy controls were performed.
Results: Increased levels of serum pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-2R, were detected in four patients. IHC staining and WB indicated significantly increased expression of cell adhesion molecules in blood vessels or inflammatory cells within the perimysium in muscle and fascia tissues of patients with myofasciitis compared to controls.
Conclusion: The up-regulation of CAMs in myofasciitis indicates endothelial activation, which may be potential therapy targets for the treatment of myofasciitis.
Keywords: cell adhesion molecules; dysregulated immune response; endothelial activation; myofasciitis; myopathy.
Copyright © 2023 Ma, Gao, Xu, Bi, Ji and Bu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be made as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Macrophagic myofasciitis: description and etiopathogenic hypotheses. Study and Research Group on Acquired and Dysimmunity-related Muscular Diseases (GERMMAD) of the French Association against Myopathies (AFM)].Rev Med Interne. 1999 Jun;20(6):483-9. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(99)80083-6. Rev Med Interne. 1999. PMID: 10422140 French.
-
[Macrophagic myofasciitis. Study and Research Group on Acquired and Dysimmunity-related muscular diseases (GERMMAD)].Presse Med. 2000 Feb 5;29(4):203-8. Presse Med. 2000. PMID: 10705901 Review. French.
-
An MRI study of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced musculoskeletal manifestations myofasciitis is the prominent imaging finding.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 May 1;59(5):1041-1050. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez361. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 32344435
-
[Coexistence of dermatomyositis and macrophagic myofasciitis].Presse Med. 2005 Mar 26;34(6):438-40. doi: 10.1016/s0755-4982(05)83938-7. Presse Med. 2005. PMID: 15902874 French.
-
[Lessons from macrophagic myofasciitis: towards definition of a vaccine adjuvant-related syndrome].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2003 Feb;159(2):162-4. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2003. PMID: 12660567 Review. French.
References
-
- Turkcapar N, Sak SD, Saatci M, Duman M, Olmez U. Vasculitis and expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and E-selectin in salivary glands of patients with Sjögren's syndrome. J Rheumatol. (2005) 32:1063–70. PMID: - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

