Systemic lupus erythematosus: latest insight into etiopathogenesis
- PMID: 37226016
- PMCID: PMC10208557
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-023-05346-x
Systemic lupus erythematosus: latest insight into etiopathogenesis
Abstract
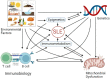
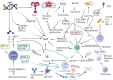
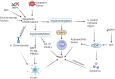
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disorder of unknown etiology. Multifactorial interaction among various susceptible factors such as environmental, hormonal, and genetic factors makes it more heterogeneous and complex. Genetic and epigenetic modifications have been realized to regulate the immunobiology of lupus through environmental modifications such as diet and nutrition. Although these interactions may vary from population to population, the understanding of these risk factors can enhance the perception of the mechanistic basis of lupus etiology. To recognize the recent advances in lupus, an electronic search was conducted among search engines such as Google Scholar and PubMed, where we found about 30.4% publications of total studies related to genetics and epigenetics, 33.5% publications related to immunobiology and 34% related to environmental factors. These outcomes suggested that management of diet and lifestyle have a direct relationship with the severity of lupus that influence via modulating the complex interaction among genetics and immunobiology. The present review emphasizes the knowledge about the multifactorial interactions between various susceptible factors based on recent advances that will further update the understanding of mechanisms involved in disease pathoetiology. Knowledge of these mechanisms will further assist in the creation of novel diagnostic and therapeutic options.
Keywords: Environmental factors; Epigenetics; Etiology; Immunobiology; Lupus; Multifactorial interactions.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenetic involvement in etiopathogenesis and implications in treatment of systemic lupus erythematous.Inflamm Res. 2017 Dec;66(12):1057-1073. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1082-y. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Inflamm Res. 2017. PMID: 28741130 Review.
-
Aberrant Epigenetic Regulation in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Its Implication in Precision Medicine.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2016;149(3):141-155. doi: 10.1159/000448793. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2016. PMID: 27607472
-
Epigenetic Alterations in Immune Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Therapeutic Implications.Cells. 2022 Feb 1;11(3):506. doi: 10.3390/cells11030506. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenetics of systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive review.J Autoimmun. 2015 Nov;64:125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.08.004. Epub 2015 Aug 29. J Autoimmun. 2015. PMID: 26324017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Epigenetics of Lupus Erythematosus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1253:185-207. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3449-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32445096 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of Anifrolumab in Moderate-to-Severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Cureus. 2024 Jul 6;16(7):e63966. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63966. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39104974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Modulators in Cardiovascular Complications of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 25;11(12):3142. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123142. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of vitamin D in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus - a double pawn in the immune and microbial balance.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 23;15:1373904. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1373904. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38715605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunosensors for Autoimmune-Disease-Related Biomarkers: A Literature Review.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;23(15):6770. doi: 10.3390/s23156770. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus along with Metabolic Syndrome.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 29;13(7):1988. doi: 10.3390/jcm13071988. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38610754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alaanzy MT, Alsaffar JM, Bari AA. Evaluate the correlation between antioxidant capacity and interferon Γ level with the disease activity of Sle patients in Iraqi Woman. Indian J Public Health Res Dev. 2020;11(1):1278–1282. doi: 10.37506/v11/i1/2020/ijphrd/194018. - DOI
-
- Terahara N. Flavonoids in foods: a review. Nat Prod Commun. 2015;10(3):19345781501000334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

