Inhibition of discoidin domain receptor (DDR)-1 with nilotinib alters CSF miRNAs and is associated with reduced inflammation and vascular fibrosis in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37194065
- PMCID: PMC10186647
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-023-02802-0
Inhibition of discoidin domain receptor (DDR)-1 with nilotinib alters CSF miRNAs and is associated with reduced inflammation and vascular fibrosis in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
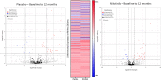
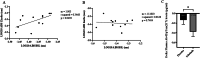
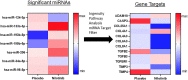
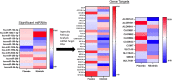
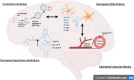
Discoidin Domain Receptor (DDR)-1 is activated by collagen. Nilotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is FDA-approved for leukemia and potently inhibits DDR-1. Individuals diagnosed with mild-moderate Alzheimer's disease (AD) treated with nilotinib (versus placebo) for 12 months showed reduction of amyloid plaque and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) amyloid, and attenuation of hippocampal volume loss. However, the mechanisms are unclear. Here, we explored unbiased next generation whole genome miRNA sequencing from AD patients CSF and miRNAs were matched with their corresponding mRNAs using gene ontology. Changes in CSF miRNAs were confirmed via measurement of CSF DDR1 activity and plasma levels of AD biomarkers. Approximately 1050 miRNAs are detected in the CSF but only 17 miRNAs are specifically altered between baseline and 12-month treatment with nilotinib versus placebo. Treatment with nilotinib significantly reduces collagen and DDR1 gene expression (upregulated in AD brain), in association with inhibition of CSF DDR1. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukins and chemokines are reduced along with caspase-3 gene expression. Specific genes that indicate vascular fibrosis, e.g., collagen, Transforming Growth Factors (TGFs) and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteases (TIMPs) are altered by DDR1 inhibition with nilotinib. Specific changes in vesicular transport, including the neurotransmitters dopamine and acetylcholine, and autophagy genes, including ATGs, indicate facilitation of autophagic flux and cellular trafficking. Inhibition of DDR1 with nilotinib may be a safe and effective adjunct treatment strategy involving an oral drug that enters the CNS and adequately engages its target. DDR1 inhibition with nilotinib exhibits multi-modal effects not only on amyloid and tau clearance but also on anti-inflammatory markers that may reduce cerebrovascular fibrosis.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Chemokines; Collagen; Cytokines; Discoidin domain receptor 1; MicroRNAs; Nilotinib.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.M. is an inventor on several US and international Georgetown University patents to use nilotinib and other tyrosine kinase inhibitors as a treatment for neurodegenerative diseases. Georgetown University and C.M are shareholders in KeifeRX LLC, a biopharmaceutical company, from which C.M. receives consulting fees and is a co-founder. C.M. receives consulting fees from SkyBio LLC and research grants from NIH–NIA and Sun Pharmaceuticals Advanced Research Corporation (SPARC). RST reports research support to Georgetown University from Alector, Biogen, Eisai, Janssen, Lilly, Roche/Genentech, Vaccinex, and Vivoryon. The remaining authors have no potential competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alteration of Autophagy and Glial Activity in Nilotinib-Treated Huntington's Disease Patients.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 6;12(12):1225. doi: 10.3390/metabo12121225. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36557263 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of collagen-induced discoidin domain receptor 1 and 2 activation by imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 3;599(1-3):44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.10.014. Epub 2008 Oct 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18938156
-
Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 is a therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Oct 10;29(17):2882-2898. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa177. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32776088 Free PMC article.
-
Discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) kinase as target for structure-based drug discovery.Drug Discov Today. 2015 Feb;20(2):255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2014.09.025. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Drug Discov Today. 2015. PMID: 25284748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of Discoidin Domain Receptor (DDR) Kinases for Cancer and Inflammation.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 10;11(11):1671. doi: 10.3390/biom11111671. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tyrosine kinases: multifaceted receptors at the intersection of several neurodegenerative disease-associated processes.Front Dement. 2024 Aug 16;3:1458038. doi: 10.3389/frdem.2024.1458038. eCollection 2024. Front Dement. 2024. PMID: 39221072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nilotinib as a Prospective Treatment for Alzheimer's Disease: Effect on Proteins Involved in Neurodegeneration and Neuronal Homeostasis.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;14(10):1241. doi: 10.3390/life14101241. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459541 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian genome-wide TWAS with reference transcriptomic data of brain and blood tissues identified 141 risk genes for Alzheimer's disease dementia.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Jun 1;16(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01488-7. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38824563 Free PMC article.
-
c-KIT inhibitors reduce pathology and improve behavior in the Tg(SwDI) model of Alzheimer's disease.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Jul 15;7(10):e202402625. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202402625. Print 2024 Oct. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39009412 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Action Kinase Inhibitors Influence p38α MAP Kinase Dephosphorylation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 8:2024.05.15.594272. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.15.594272. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jan 7;122(1):e2415150122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2415150122 PMID: 39149408 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Snyder HM, Corriveau RA, Craft S, Faber JE, Greenberg SM, Knopman D, Lamb BT, Montine TJ, Nedergaard M, Schaffer CB, et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia including Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015;11:710–717. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2014.10.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

